Click here to Visit Facebook Page
Whooping cough, medically known as pertussis, is a highly contagious respiratory infection caused by the bacterium Bordetella pertussis. While it can affect individuals of all ages, it is particularly dangerous for infants and young children. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the symptoms, treatment options, and prevention methods for whooping cough.
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
What is Whooping Cough?
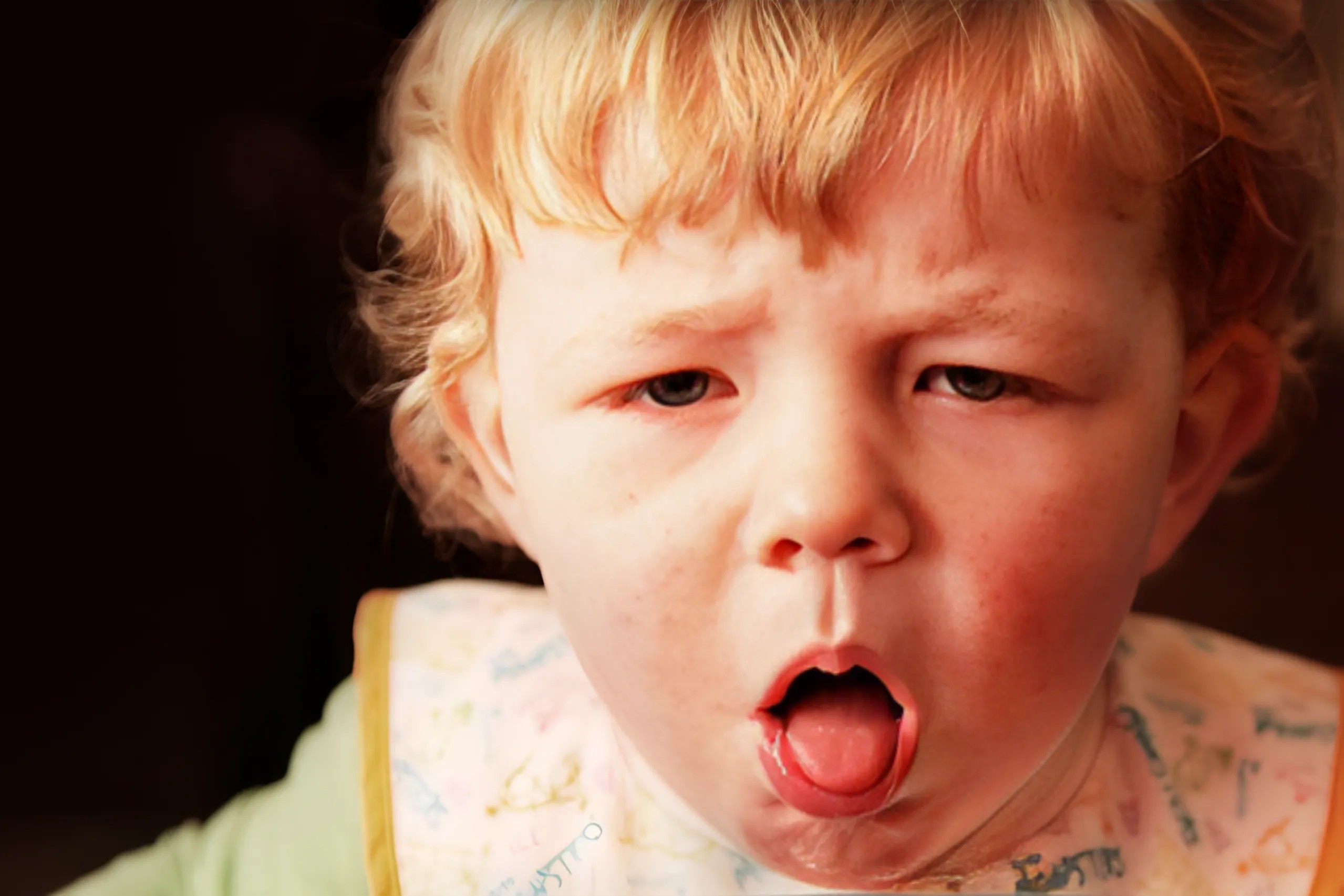
Whooping cough earned its name from the distinctive “whooping” sound that infected individuals make as they gasp for air after a coughing fit. The disease is primarily spread through respiratory droplets when an infected person coughs or sneezes. It can also spread through contact with contaminated surfaces.
Symptoms of Whooping Cough
The symptoms of whooping cough typically develop in stages and can last for several weeks. The initial symptoms resemble those of a common cold and may include:
1. Runny nose
2. Sneezing
3. Low-grade fever
4. Mild cough
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
As the infection progresses, the cough becomes more severe and is characterized by:
1. Frequent, uncontrollable coughing fits
2. Difficulty breathing
3. The distinctive “whooping” sound as the individual gasps for air
In infants, whooping cough can be particularly severe, leading to complications such as pneumonia, seizures, brain damage, or even death.
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosing whooping cough typically involves a combination of physical examination, medical history review, and laboratory tests. Nasopharyngeal swabs or blood tests can help confirm the presence of the Bordetella pertussis bacterium.
Treatment for whooping cough usually involves a course of antibiotics, such as azithromycin or erythromycin, to eradicate the bacteria and reduce the severity and duration of symptoms. In severe cases, hospitalization may be necessary, especially for infants and young children who are at higher risk of complications.
Additionally, supportive care measures may be recommended to alleviate symptoms and prevent complications. These may include:
1. Using a humidifier to ease coughing and soothe the airways
2. Drinking plenty of fluids to stay hydrated
3. Getting plenty of rest
It is essential to complete the full course of antibiotics as prescribed by a healthcare professional, even if symptoms improve, to prevent the spread of the infection to others.
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
Prevention Strategies
Preventing whooping cough primarily involves vaccination and practicing good hygiene. Vaccination is the most effective way to protect against the disease, and the pertussis vaccine is typically administered as part of the DTaP (diphtheria, tetanus, and acellular pertussis) vaccine series, starting in infancy.
In addition to vaccination, the following measures can help prevent the spread of whooping cough:
1. Frequent handwashing with soap and water
2. Covering mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing
3. Avoiding close contact with individuals who are sick
4. Staying home from school or work when ill
It is particularly crucial for pregnant women to receive the Tdap (tetanus, diphtheria, and acellular pertussis) vaccine during each pregnancy to protect themselves and pass on immunity to their unborn babies.
Conclusion
Whooping cough is a serious respiratory infection that can have severe consequences, especially for infants and young children. Recognizing the symptoms, seeking prompt medical attention, and following prevention strategies, including vaccination, are essential steps in controlling the spread of the disease and protecting vulnerable populations. By staying informed and taking proactive measures, we can work together to prevent the spread of whooping cough and keep our communities healthy and safe.