Click here to Visit Facebook Page
Tuberculosis (TB) remains a significant global health concern, affecting millions of people each year. This infectious disease primarily targets the lungs but can also affect other parts of the body. In this blog, we’ll delve into the different types of TB, its symptoms, methods of diagnosis, and available treatment options.
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
Types of Tuberculosis
1. Pulmonary TB:
This is the most common form of TB, affecting the lungs. Symptoms include persistent cough, chest pain, coughing up blood, fatigue, fever, and weight loss.
2. Extrapulmonary TB:
TB can affect other parts of the body besides the lungs, such as the kidneys, spine, or brain. Symptoms vary depending on the area affected but may include swelling, pain, and neurological symptoms.
Symptoms of Tuberculosis
TB symptoms can be subtle and may not appear immediately. They often develop gradually and may include:
– Persistent cough lasting more than three weeks
– Coughing up blood
– Chest pain
– Fatigue
– Fever and chills
– Night sweats
– Loss of appetite
– Unintentional weight loss
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
Diagnosis of Tuberculosis
Diagnosing TB involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests. Common diagnostic methods include:
1. Tuberculin Skin Test (TST):
A small amount of TB protein is injected under the skin, and if a person has been infected with TB, their immune system will react, causing a bump or redness at the injection site.
2. Interferon-Gamma Release Assays (IGRAs):
These blood tests detect the presence of TB infection by measuring the immune response to TB bacteria.
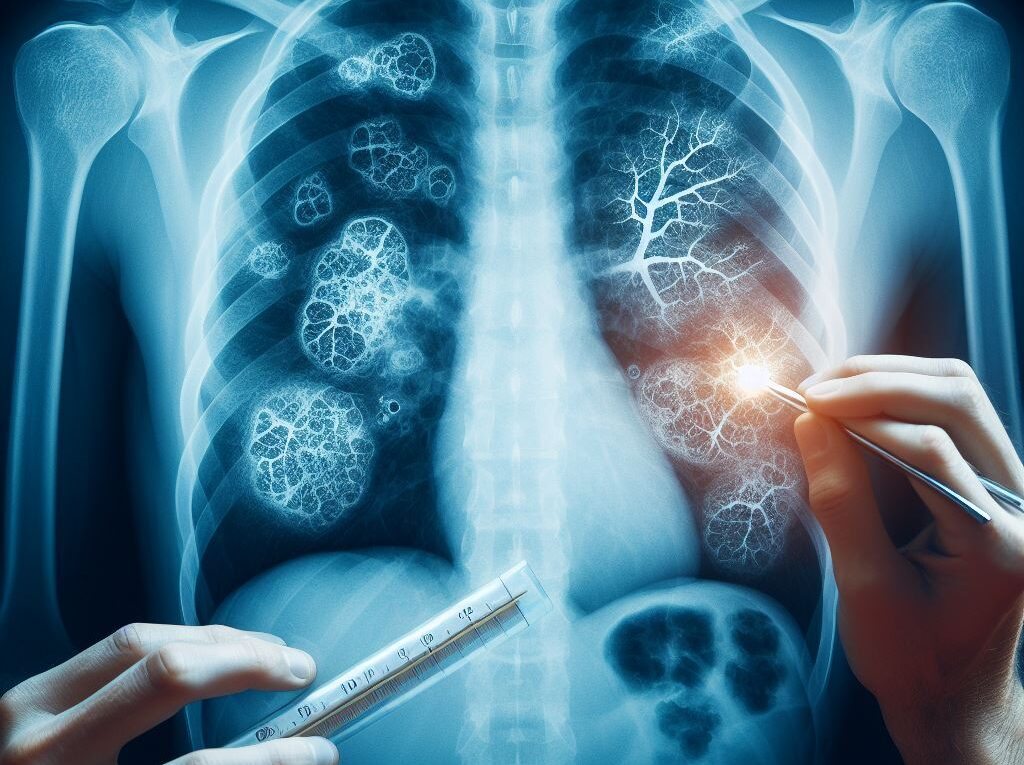
3. Chest X-ray:
This imaging test helps detect abnormalities in the lungs caused by TB infection.
4. Sputum Smear Microscopy:
A sample of sputum (mucus coughed up from the lungs) is examined under a microscope to check for the presence of TB bacteria.
5. Molecular Testing (PCR):
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) tests can quickly detect TB bacteria in sputum or other bodily fluids.
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
Treatment of Tuberculosis
TB is treated with a combination of antibiotics over a prolonged period, typically 6 to 9 months. The most commonly used medications include:
– Isoniazid (INH)
– Rifampin (RIF)
– Pyrazinamide (PZA)
– Ethambutol (EMB)
It’s crucial to complete the full course of treatment to ensure the bacteria are completely eradicated and to prevent the development of drug-resistant strains.
In conclusion, tuberculosis is a serious infectious disease that requires prompt diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Understanding its types, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options is essential in combating this global health threat. Early detection and proper management are key to preventing the spread of TB and reducing its impact on individuals and communities worldwide.