Click here to Visit Facebook Page
Bronchitis is a common respiratory condition that affects millions of people worldwide each year. It can be acute or chronic and can cause discomfort and distress. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore what bronchitis is, its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and prevention strategies.
What is Bronchitis?
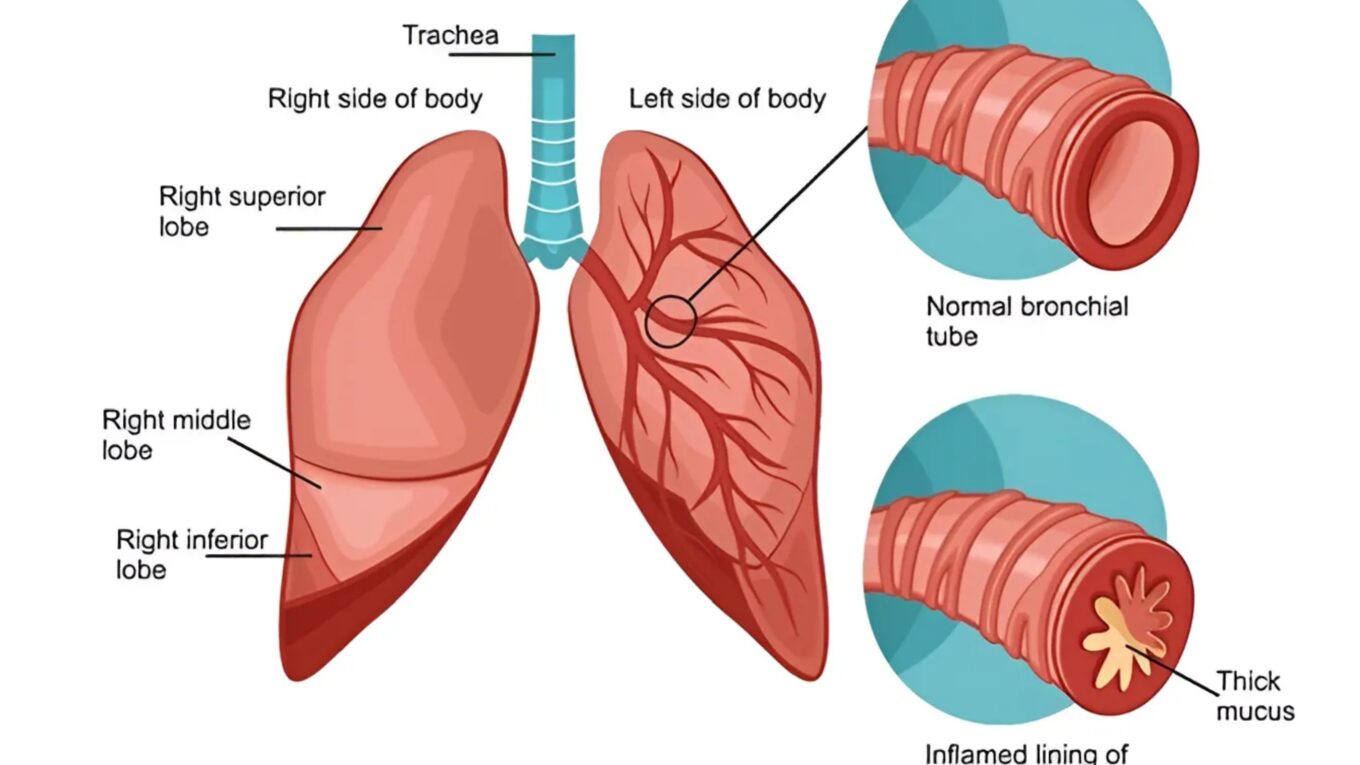
Bronchitis is an inflammation of the bronchial tubes, which are the air passages that carry air to the lungs. When these tubes become inflamed, they produce excess mucus, leading to coughing, difficulty breathing, and other symptoms.
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
Types of Bronchitis:
1. Acute Bronchitis: This type of bronchitis typically develops as a result of a viral infection, such as the common cold or flu. It usually lasts for a few weeks and resolves on its own with rest and hydration.
2. Chronic Bronchitis: Chronic bronchitis is characterized by persistent inflammation of the bronchial tubes. It is often associated with long-term exposure to irritants such as cigarette smoke, air pollution, or industrial fumes. Chronic bronchitis is a type of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and requires ongoing management.
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
Causes of Bronchitis:
– Viral Infections: The most common cause of acute bronchitis is viral infections, including the influenza virus, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), and rhinovirus (which causes the common cold).
– Bacterial Infections: In some cases, acute bronchitis may be caused by bacterial infections, such as Bordetella pertussis (which causes whooping cough) or Mycoplasma pneumoniae.
– Smoking: Tobacco smoke is a significant irritant that can lead to chronic bronchitis. Smokers are at a higher risk of developing chronic bronchitis compared to non-smokers.
– Environmental Factors: Exposure to air pollution, dust, fumes, and other airborne irritants can increase the risk of developing bronchitis.
– Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD): Chronic acid reflux can irritate the lining of the bronchial tubes, leading to bronchitis symptoms.
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
Symptoms of Bronchitis:
– Persistent cough with or without mucus production
– Wheezing or chest tightness
– Shortness of breath
– Sore throat
– Fatigue
– Mild fever and chills (in some cases)
Diagnosis of Bronchitis:
Diagnosing bronchitis typically involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests, including:
– Physical Examination: Your doctor will listen to your lungs with a stethoscope to check for abnormal sounds such as wheezing or crackles.
– Chest X-ray: A chest X-ray may be ordered to rule out other respiratory conditions such as pneumonia.
– Sputum Culture: If bacterial infection is suspected, a sample of mucus (sputum) may be collected and sent to a laboratory for analysis.
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
Treatment of Bronchitis:
Treatment for bronchitis depends on the type and severity of the condition. In most cases, acute bronchitis can be managed with rest, hydration, and over-the-counter medications to relieve symptoms such as cough and fever. Antibiotics are not usually prescribed for viral bronchitis unless there is evidence of a bacterial infection.
For chronic bronchitis, treatment may include:
– Bronchodilators: These medications help open the airways and improve breathing.
– Corticosteroids: Inhaled corticosteroids may be prescribed to reduce inflammation in the airways.
– Oxygen Therapy: For severe cases of chronic bronchitis, supplemental oxygen may be necessary to maintain adequate oxygen levels in the blood.
– Pulmonary Rehabilitation: This comprehensive program includes exercise training, education, and support to improve lung function and quality of life.
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
Prevention of Bronchitis:
While it may not be possible to prevent all cases of bronchitis, there are steps you can take to reduce your risk:
– Quit Smoking: If you smoke, quitting is the single most effective way to prevent bronchitis and other respiratory conditions.
– Avoid Respiratory Irritants: Minimize exposure to air pollution, dust, smoke, and other airborne irritants.
– Practice Good Hygiene: Wash your hands frequently, avoid close contact with sick individuals, and cover your mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing to prevent the spread of respiratory infections.
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
Conclusion:
Bronchitis is a common respiratory condition that can cause significant discomfort and disruption to daily life. Whether acute or chronic, early diagnosis and appropriate treatment are essential for managing symptoms and preventing complications. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for bronchitis, individuals can take proactive steps to protect their respiratory health and well-being. If you experience persistent coughing or other respiratory symptoms, consult with your healthcare provider for proper evaluation and management.