Click here to Visit Facebook Page
Introduction:
Fungal infections, caused by various types of fungi, are common occurrences that can affect different parts of the body, including the skin, nails, hair, and internal organs.
These infections range from mild to severe and can impact individuals of all ages and backgrounds.
Understanding the causes, symptoms, treatment options, and prevention strategies for fungal infections is crucial for effective management and maintaining overall health and well-being.
What are Fungal Infections?
Fungal infections, also known as mycoses, are caused by fungi that thrive in warm, moist environments.
Fungi are ubiquitous in nature, and while many are harmless or beneficial, some can cause infections
when they overgrow or invade the body’s tissues. Fungal infections can be superficial, affecting only the skin, hair, or nails,
or they can be systemic, involving internal organs and potentially leading to serious health complications.
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
Types of Fungal Infections:
1.Athlete’s Foot (Tinea Pedis): A common fungal infection that affects the skin between the toes and on the soles of the feet, causing itching, redness, cracking, and peeling.
2.Ringworm (Tinea Corporis): Characterized by circular, red, scaly patches on the skin, ringworm can occur on various parts of the body,
including the scalp (tinea capitis), body (tinea corporis), and groin (tinea cruris).
3.Yeast Infections: Caused by the overgrowth of Candida species, yeast infections can affect the skin,
mouth (oral thrush), genitals (vaginal yeast infection), and other mucous membranes, leading to itching, burning, and discharge.
4.Jock Itch (Tinea Cruris): Similar to athlete’s foot but occurring in the groin area, jock itch causes redness, itching, and a rash in the groin folds and genitals.
5.Fungal Nail Infections: Also known as onychomycosis, fungal nail infections affect the toenails and fingernails, causing thickening, discoloration, crumbling, and separation from the nail bed.
6.Systemic Fungal Infections: These infections occur when fungi enter the bloodstream or invade internal organs,
posing a serious risk to individuals with weakened immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS, cancer, or undergoing immunosuppressive therapy.
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
Causes of Fungal Infections:
Fungal infections are typically caused by exposure to fungi in the environment or through direct contact with infected individuals or surfaces.
Several factors can increase the risk of developing fungal infections, including:
1.Warm, Moist Environments: Fungi thrive in warm, humid conditions, making areas such as locker rooms, swimming pools, and shoes conducive to fungal growth.
2.Weakened Immune System: Individuals with weakened immune systems, due to conditions such as HIV/AIDS, diabetes, or autoimmune disorders, are more susceptible to fungal infections.
3.Poor Hygiene: Inadequate personal hygiene, such as not washing hands regularly, sharing personal items (towels, combs, etc.), or wearing damp clothing, can increase the risk of fungal infections.
4.Skin-to-Skin Contact: Close contact with an infected person or animal, as well as contact with contaminated surfaces or objects, can transmit fungal infections.
5.Certain Medications: Prolonged use of antibiotics, corticosteroids, or immunosuppressive drugs can disrupt the body’s natural balance of microorganisms, increasing the risk of fungal overgrowth.
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
Symptoms of Fungal Infections:
The symptoms of fungal infections vary depending on the type and location of the infection but may include:
1.Itching: Persistent itching, burning, or tingling sensation in the affected area.
2.Redness and Inflammation: Skin redness, irritation, and inflammation, often accompanied by swelling and tenderness.
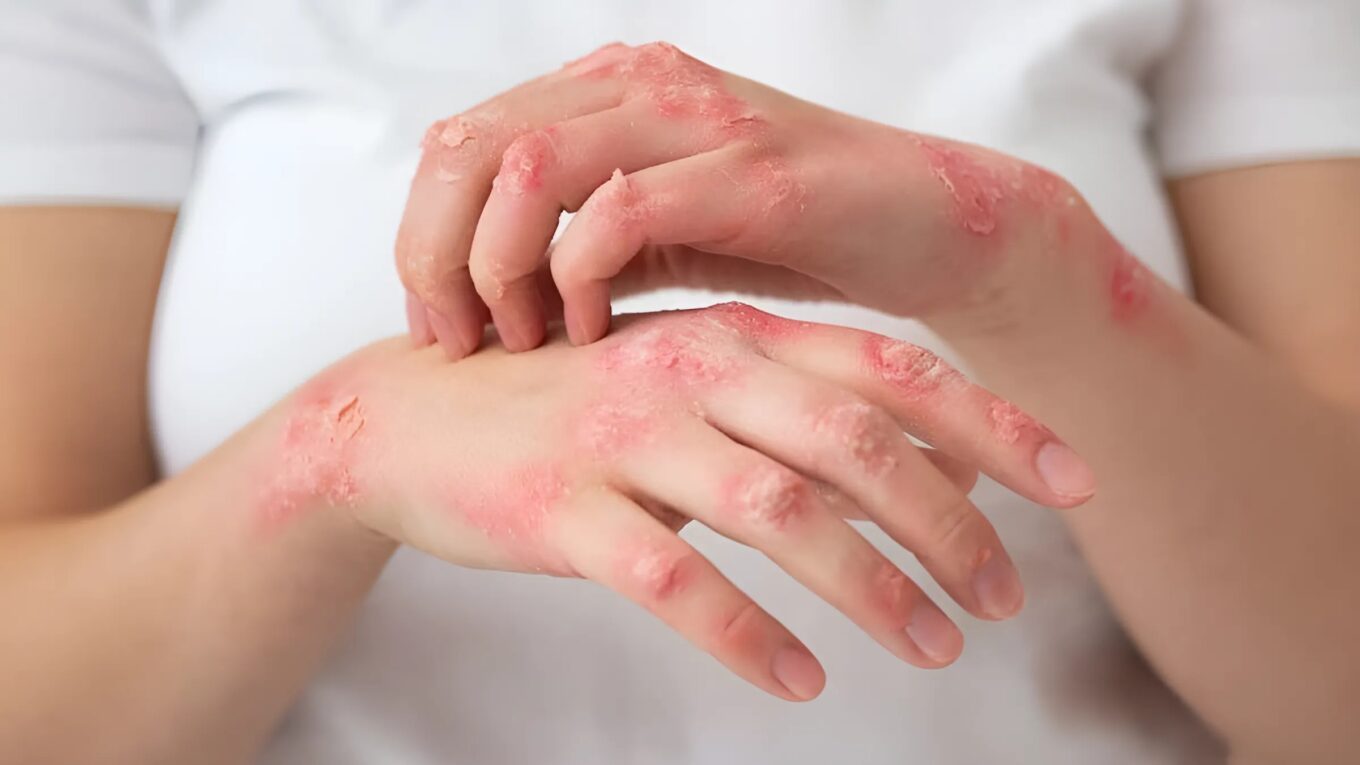
3.Rash or Lesions: Raised, red, scaly patches, blisters, or lesions on the skin, scalp, or mucous membranes.
4.Discharge: Abnormal discharge, such as white, cottage cheese-like discharge in the case of vaginal yeast infections.
5.Changes in Nails: Thickening, discoloration, brittleness, or deformation of the nails in cases of fungal nail infections.
6.Systemic Symptoms: In severe cases of systemic fungal infections, symptoms may include fever, chills, fatigue, cough, difficulty breathing, and organ dysfunction.
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
Treatment Options:
Treatment for fungal infections depends on the type, severity, and location of the infection but may include:
1.Antifungal Medications: Topical or oral antifungal medications, such as clotrimazole, miconazole, terbinafine, fluconazole, or itraconazole, are commonly used to treat fungal infections.
These medications work by inhibiting the growth and spread of fungi.
2.Topical Creams and Ointments: Over-the-counter or prescription-strength antifungal creams, ointments, powders, or sprays can help relieve symptoms and eradicate fungal infections on the skin, nails, or mucous membranes.
3.Oral Medications: Oral antifungal medications may be prescribed for severe or systemic fungal infections, especially in cases of nail infections or infections resistant to topical treatment.
4.Home Remedies: Some individuals may find relief from fungal infections using home remedies such as tea tree oil, apple cider vinegar, yogurt, or garlic, although scientific evidence supporting their effectiveness is limited.
5.Procedures: In cases of severe or recurrent fungal nail infections, surgical procedures such as nail removal or laser therapy may be considered to remove the infected nail tissue.
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
Prevention Strategies:
Preventing fungal infections involves adopting good hygiene practices and minimizing exposure to fungi.
Consider the following preventive measures:
1.Keep Skin Clean and Dry: Wash regularly with soap and water, especially after sweating or coming into contact with contaminated surfaces.
2.Wear Clean, Breathable Clothing: Choose loose-fitting, breathable clothing made from natural fibers such as cotton to reduce moisture and promote airflow.
3.Practice Good Foot Hygiene: Keep feet clean and dry, wear clean socks and shoes, and avoid walking barefoot in public areas such as locker rooms and swimming pools.
4.Avoid Sharing Personal Items: Do not share towels, socks, shoes, combs, or other personal items with others to prevent the spread of fungal infections.
5.Use Antifungal Products: Apply antifungal powders, sprays, or creams to susceptible areas, such as feet or groin, to prevent fungal growth.
6.Protect Against Nail Infections: Trim nails straight across, keep them clean and dry, and avoid picking or biting nails to reduce the risk of fungal nail infections.
7.Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle: Eat a balanced diet, exercise regularly, get enough sleep, and manage stress to support overall immune function and reduce the risk of fungal infections.