Click here to Visit Facebook Page
What is Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)?
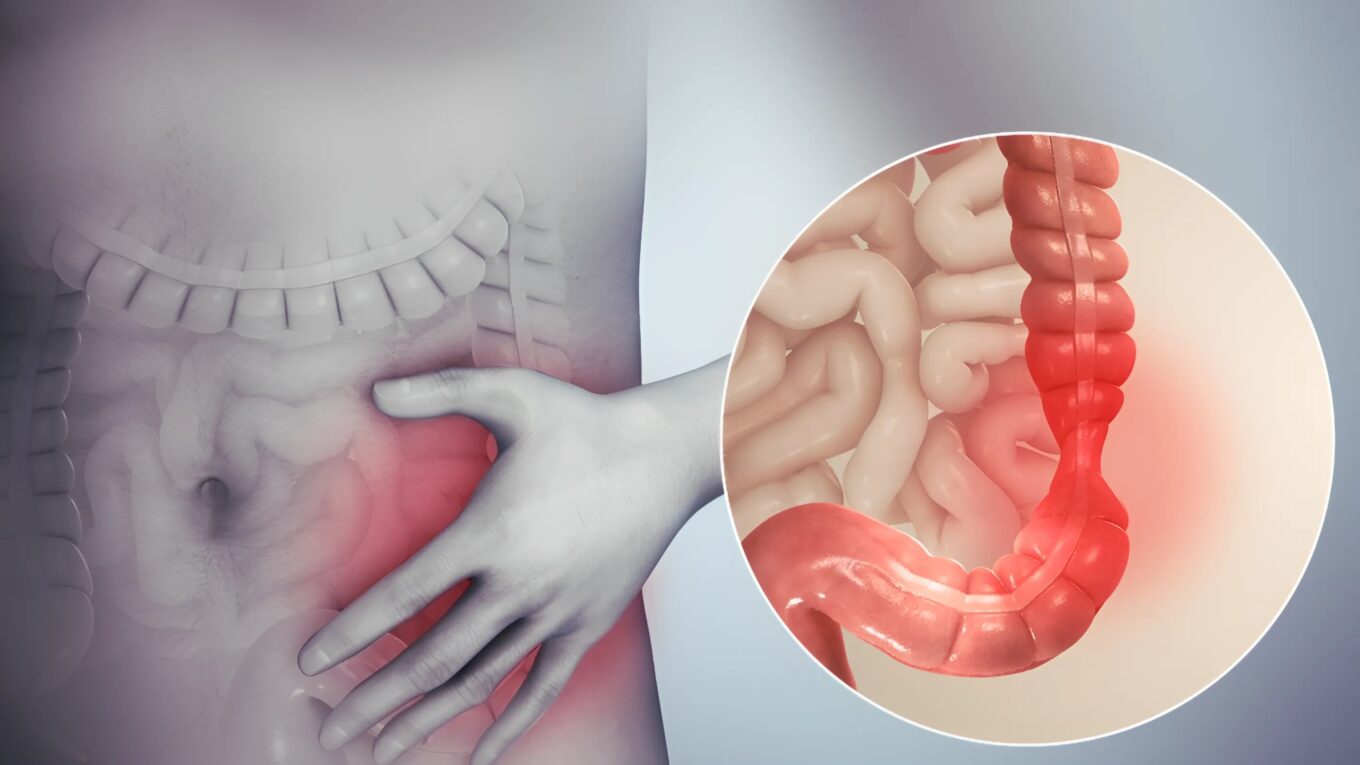
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) presents a complex interplay of symptoms and management strategies, affecting millions worldwide. This gastrointestinal disorder manifests in various forms, each characterized by distinct symptoms, contributing factors, and treatment approaches. Let’s embark on an in-depth exploration of IBS, dissecting its types, symptoms, causes, treatment modalities, and prevention strategies.
Types of IBS:
1. IBS-D (Diarrhea-Predominant): Individuals with IBS-D experience frequent bouts of diarrhea, urgency, and loose stools. The predominant symptomatology revolves around diarrhea-related manifestations, disrupting daily routines and instilling a sense of unpredictability.
2. IBS-C (Constipation-Predominant): In contrast, IBS-C manifests as infrequent bowel movements, accompanied by straining, discomfort, and a sense of incomplete evacuation. Constipation takes center stage in this subtype, posing challenges in bowel regularity and overall well-being.
3. IBS-M (Mixed): IBS-M entails a fluctuation between diarrhea and constipation, leaving individuals oscillating between unpredictable bowel habits. The erratic nature of symptoms complicates management, requiring tailored approaches to address both diarrhea and constipation manifestations.
4. IBS-U (Unsubtyped): IBS-U encompasses cases where symptoms defy classification into the aforementioned subtypes. Individuals with unsubtyped IBS may present with a combination of symptoms or exhibit atypical symptomatology, necessitating personalized management strategies.
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
Symptoms of IBS:
Common symptoms of IBS include:
– Abdominal pain or discomfort
– Bloating and gas
– Altered bowel habits (diarrhea, constipation, or both)
– Urgency to have a bowel movement
– Feeling of incomplete evacuation
– Mucus in the stool
These symptoms vary in intensity and duration, contributing to the unpredictable
nature of IBS and its impact on daily functioning and quality of life.
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
Causes of IBS:
The exact etiology of IBS remains elusive, with a multitude of factors implicated in its pathogenesis. Potential contributors include:
– Abnormal gastrointestinal motility: Dysregulated movement of the intestines can lead to altered bowel habits characteristic of IBS.
– Visceral hypersensitivity: Heightened sensitivity to internal organ sensations may amplify pain perception in individuals with IBS.
– Gut-brain axis dysfunction: Communication disruptions between the gut and brain can influence gastrointestinal function and symptom manifestation.
– Microbiota alterations: Imbalances in the gut microbiome may contribute to symptom exacerbation in some individuals with IBS.
– Psychological factors: Stress, anxiety, and depression can exacerbate IBS symptoms, highlighting the intricate interplay between mental health and gastrointestinal function.
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
Treatment of IBS:
Managing IBS entails a multifaceted approach addressing symptomatology, underlying factors, and individual patient needs. Treatment modalities include:
– Dietary modifications: Adjusting dietary intake to avoid trigger foods and incorporating fiber-rich options can help alleviate symptoms.
– Medications: Antispasmodics, antidiarrheals, laxatives, and antidepressants may be prescribed to manage specific symptoms and promote bowel regularity.
– Behavioral therapies: Stress management techniques, cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), and relaxation exercises can mitigate psychological distress and symptom exacerbation.
– Probiotics: Certain probiotic strains may offer symptomatic relief by modulating gut microbiota composition and function.
– Alternative therapies: Acupuncture, herbal remedies, and hypnotherapy are among the complementary approaches that some individuals find beneficial in managing IBS symptoms.
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
Prevention Strategies for IBS:
While the prevention of IBS remains challenging due to its multifactorial nature, adopting certain lifestyle modifications and
self-care practices may help reduce symptom severity and frequency. Prevention strategies include:
– Maintaining a balanced diet: Consuming a diverse array of nutrient-rich foods and staying hydrated can support gastrointestinal health and minimize symptom exacerbation.
– Managing stress: Practicing relaxation techniques, engaging in regular physical activity, and prioritizing self-care activities can mitigate stressors known to exacerbate IBS symptoms.
– Seeking early intervention: Prompt evaluation and treatment of gastrointestinal symptoms can prevent symptom progression and improve long-term outcomes for individuals with IBS.
– Establishing a supportive healthcare team: Collaborating with healthcare providers specializing in gastrointestinal disorders can
facilitate comprehensive management and personalized care tailored to individual needs.