Click here to Visit Facebook Page
Introduction:
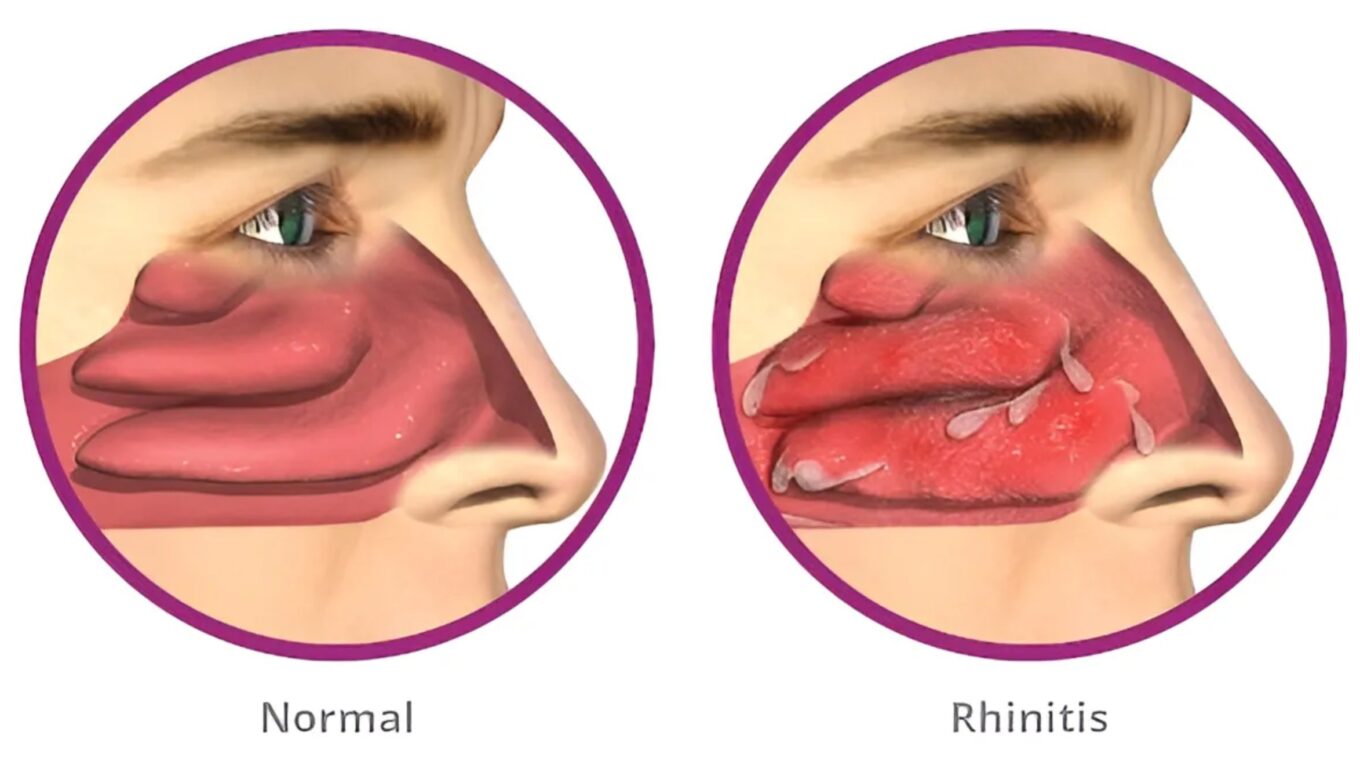
Allergic rhinitis, commonly known as hay fever, is a prevalent allergic condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It occurs when the immune system overreacts to allergens in the air, leading to inflammation and irritation of the nasal passages. This blog aims to provide a comprehensive overview of allergic rhinitis, including its symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and management strategies.
Symptoms:
The hallmark symptoms of allergic rhinitis include:
1. Sneezing: Frequent bouts of sneezing, especially upon exposure to allergens such as pollen, dust, or pet dander.
2. Nasal congestion: Stuffy or blocked nose, making it difficult to breathe through the nostrils.
3. Runny nose: Excessive production of clear, watery mucus from the nasal passages.
4. Itchy nose, throat, and eyes: Persistent itching sensation in the nose, throat, and eyes, often accompanied by redness and irritation.
5. Watery eyes: Excessive tearing or watering of the eyes, particularly in response to allergens.
These symptoms can vary in severity from mild to severe and may significantly impact the quality of life of affected individuals, interfering with sleep, work, and daily activities.
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
Causes:
Allergic rhinitis is primarily triggered by the immune system’s reaction to specific allergens. Common allergens include:
1. Pollen: Pollen from trees, grasses, and weeds is a major trigger for seasonal allergic rhinitis, which typically occurs during specific times of the year when plants are in bloom.
2. Dust mites: Microscopic organisms that thrive in household dust, bedding, and upholstered furniture can trigger year-round allergic rhinitis symptoms.
3. Pet dander: Proteins found in the skin flakes, saliva, and urine of cats, dogs, and other pets can elicit allergic reactions in susceptible individuals.
4. Mold: Indoor and outdoor mold spores can trigger allergic rhinitis, especially in damp and humid environments.
5. Other allergens: Certain foods, insect stings, and environmental pollutants may also contribute to allergic rhinitis symptoms in some individuals.
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
Diagnosis:
Diagnosing allergic rhinitis typically involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and allergy testing. Your healthcare provider may ask about your symptoms, triggers, and family history of allergies. A physical examination of the nasal passages may reveal signs of inflammation, congestion, and nasal polyps.
Allergy testing, such as skin prick tests or blood tests, can help identify specific allergens that trigger your symptoms. These tests involve exposing the skin to small amounts of allergens and observing for any allergic reactions. Identifying the allergens responsible for your symptoms is crucial for developing an effective management plan.
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
Management:
Management of allergic rhinitis focuses on reducing exposure to allergens and alleviating symptoms through various treatment options. Here are some strategies for managing allergic rhinitis:
1. Avoidance of allergens: Minimize exposure to known allergens by keeping indoor environments clean, using air purifiers, and avoiding outdoor activities during peak pollen seasons.
2. Medications: Over-the-counter and prescription medications, including antihistamines, decongestants, nasal corticosteroids, and nasal sprays, can help alleviate symptoms such as sneezing, nasal congestion, and itching.
3. Immunotherapy: Allergy shots or sublingual immunotherapy (under-the-tongue tablets) may be recommended for individuals with severe allergic rhinitis who do not respond to other treatments. These treatments involve gradually exposing the immune system to small amounts of allergens to desensitize it over time.
4. Nasal irrigation: Rinsing the nasal passages with saline solution can help flush out allergens, irritants, and mucus, providing temporary relief from congestion and sinus pressure.
5. Lifestyle modifications: Practices such as using allergen-proof pillowcases and mattress covers, keeping pets out of bedrooms, and wearing a mask when gardening or doing outdoor activities can help reduce exposure to allergens.
Conclusion:
Allergic rhinitis is a common allergic condition characterized by inflammation of the nasal passages in response to specific allergens. Understanding its symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and management strategies is essential for effectively managing the condition and improving the quality of life for affected individuals. By implementing appropriate lifestyle modifications and treatment interventions, individuals with allergic rhinitis can better control their symptoms and minimize their impact on daily life.