Click here to Visit Facebook Page
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) is a serious medical condition characterized by the gradual loss of kidney function over time. It affects millions of people worldwide and can lead to various complications if not managed properly. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of CKD.
1. What is Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)?
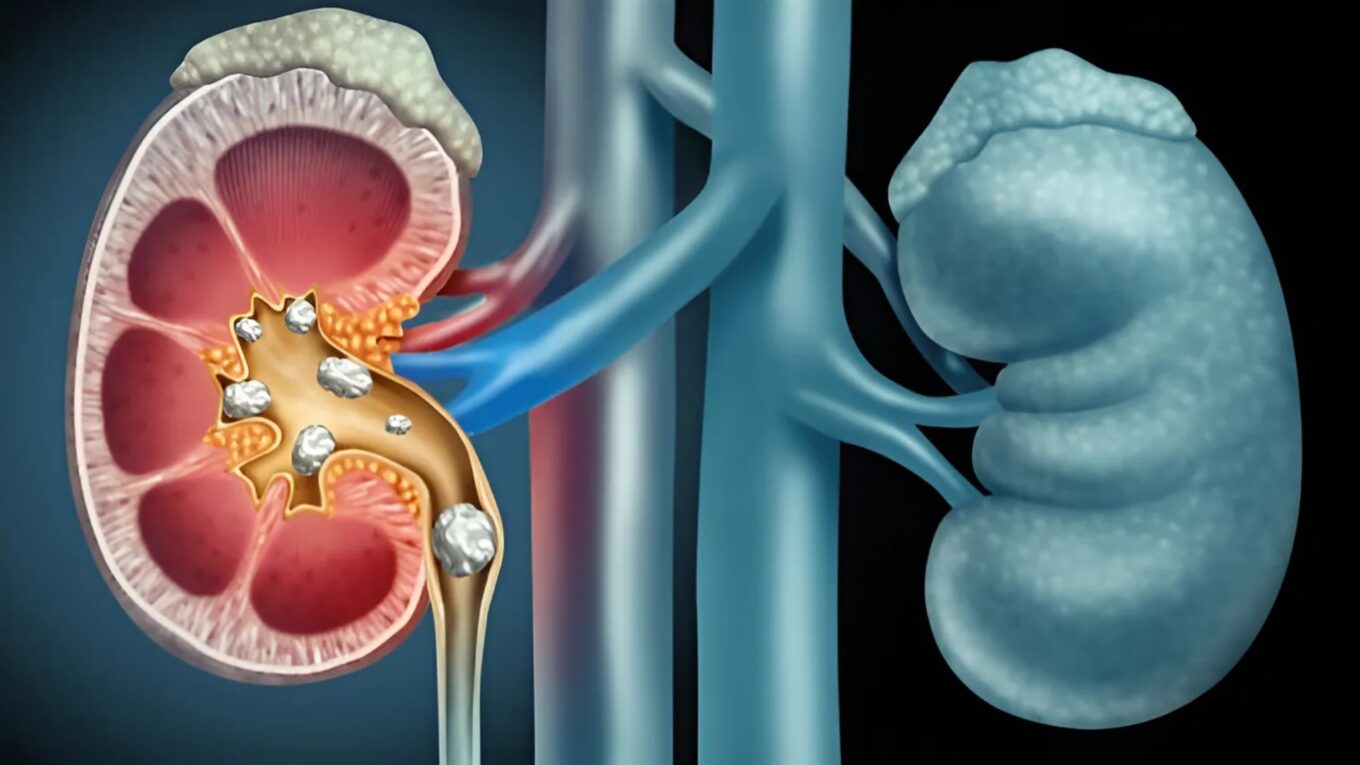
CKD is a condition in which the kidneys become damaged and cannot filter blood properly. This can lead to a buildup of waste products and excess fluids in the body. CKD is classified into five stages, with stage 1 being the mildest and stage 5 being the most severe, also known as end-stage renal disease (ESRD).
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
2. Causes of CKD:
– Diabetes: Diabetes is the leading cause of CKD. High blood sugar levels can damage the kidneys over time.
– Hypertension (High Blood Pressure): Uncontrolled high blood pressure can strain the kidneys and lead to CKD.
– Glomerulonephritis: This is inflammation of the kidney’s filtering units, called glomeruli, which can result in kidney damage.
– Polycystic Kidney Disease (PKD): PKD is a genetic disorder characterized by the growth of cysts in the kidneys, leading to CKD over time.
– Autoimmune Diseases: Conditions like lupus and rheumatoid arthritis can cause inflammation in the kidneys and contribute to CKD.
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
3. Symptoms of CKD:
In the early stages, CKD may not cause any symptoms. As the disease progresses, however, individuals may experience:
– Fatigue
– Swelling in the hands, feet, or face
– Changes in urination frequency or color
– Blood in the urine
– High blood pressure
– Nausea and vomiting
– Itching
– Loss of appetite
4. Diagnosis of CKD:
CKD is typically diagnosed through a combination of medical history, physical examination, and laboratory tests. Common tests used to diagnose CKD include:
– Blood tests to measure creatinine and glomerular filtration rate (GFR)
– Urine tests to check for protein, blood, or other abnormalities
– Imaging tests such as ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI to assess kidney structure
– Kidney biopsy in some cases to evaluate kidney tissue under a microscope
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
5. Treatment of CKD:
While there is no cure for CKD, treatment aims to slow down the progression of the disease and manage its complications. Treatment options may include:
– Medications: Medications to control blood pressure, manage blood sugar levels (for diabetic patients), and treat underlying conditions contributing to CKD.
– Dietary Changes: Following a healthy diet low in salt, potassium, and phosphorus can help reduce the workload on the kidneys.
– Lifestyle Modifications: Regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, quitting smoking, and limiting alcohol intake can all benefit kidney health.
– Dialysis: In advanced stages of CKD, dialysis may be necessary to artificially filter waste products from the blood.
– Kidney Transplant: For eligible candidates, kidney transplantation offers the best long-term outcome for individuals with ESRD.
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
6. Prevention of CKD:
Preventing CKD involves managing risk factors and adopting a healthy lifestyle. Key preventive measures include:
– Managing underlying conditions such as diabetes and hypertension through medication, lifestyle changes, and regular monitoring.
– Avoiding overuse of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and certain medications that can damage the kidneys.
– Maintaining a healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins while limiting processed foods, salt, and sugar.
– Staying hydrated by drinking an adequate amount of water daily.
– Avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption.
7. Conclusion:
Chronic Kidney Disease is a serious health condition that requires early detection and management to prevent complications and improve outcomes. By understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention strategies outlined in this guide, individuals can take proactive steps to protect their kidney health and overall well-being. Regular medical check-ups and communication with healthcare providers are essential for those at risk or already diagnosed with CKD. Remember, early intervention is key to slowing down the progression of CKD and maintaining a good quality of life.