Click here to Visit Facebook Page
Introduction:
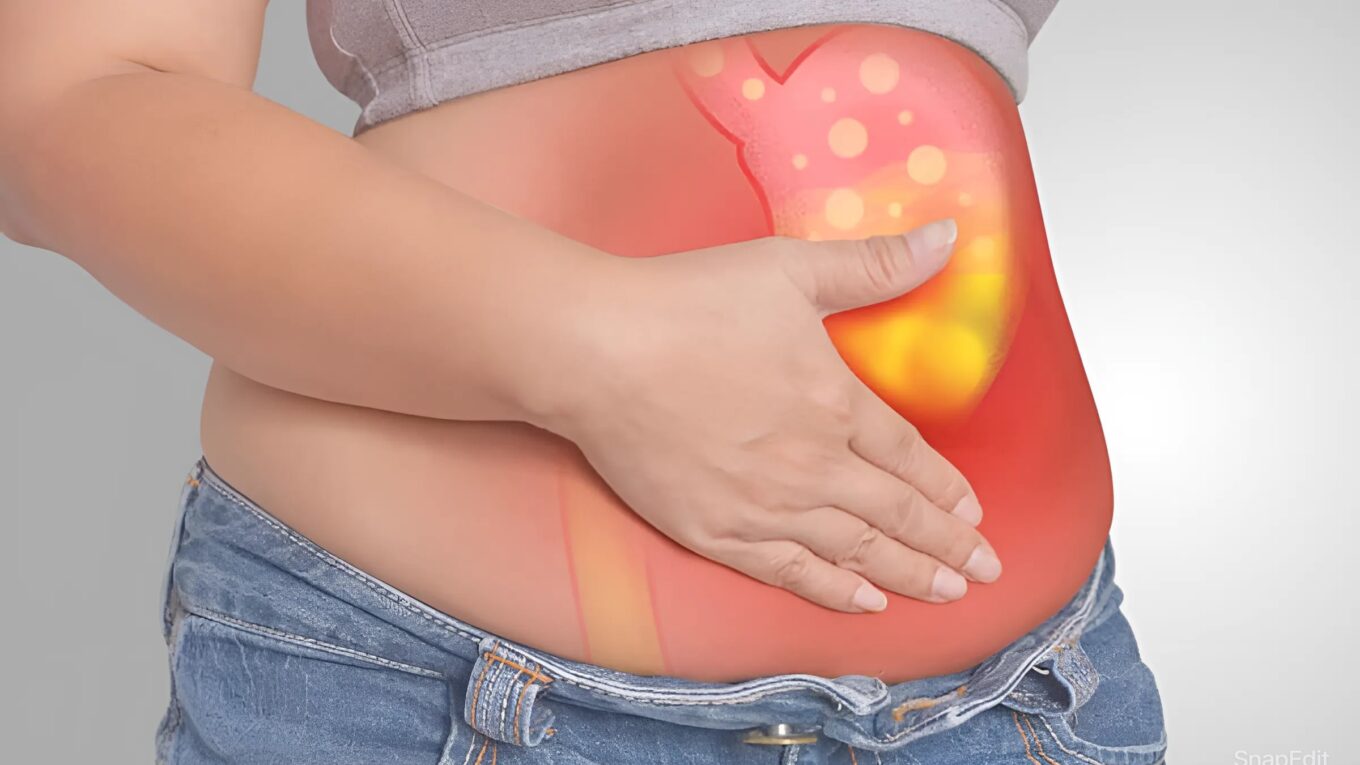
Bloating is a common and often uncomfortable sensation characterized by a feeling of fullness or tightness in the abdomen. While occasional bloating is normal, persistent or severe bloating may indicate an underlying health issue. Understanding the causes, symptoms, prevention, and treatment options for bloating is essential for managing this condition effectively.
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
Types of Bloating:
1. Gas Bloating:
Gas bloating occurs when an excessive amount of gas builds up in the digestive system, leading to discomfort, a feeling of fullness, and visible distension of the abdomen. This condition often arises from various factors, including swallowing air while eating or drinking, consuming foods that produce gas during digestion (such as beans, broccoli, and carbonated beverages), or underlying gastrointestinal issues like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) or lactose intolerance. Symptoms may vary in severity, ranging from mild discomfort to significant abdominal pain and can be managed through dietary adjustments, lifestyle changes, and, in some cases, medical intervention.
2. Water Retention Bloating:
Water retention bloating, also known as edema, occurs when excess fluid accumulates in the body’s tissues, leading to swelling, puffiness, and a feeling of heaviness. This condition can affect various parts of the body, including the hands, feet, ankles, and abdomen. It can be caused by factors such as hormonal changes, dietary habits (such as excessive salt intake), certain medications, or underlying health conditions like kidney or heart problems. Managing water retention bloating often involves lifestyle changes, such as reducing salt intake, staying hydrated, exercising regularly, and addressing any underlying medical issues.
3. Food Sensitivity Bloating:
Food sensitivity bloating occurs when your body reacts to certain foods by producing gas, causing discomfort and bloating in the digestive system. Unlike food allergies, which involve the immune system, food sensitivities typically involve difficulty digesting specific foods. Common triggers include gluten, dairy, certain fruits and vegetables, and artificial sweeteners. Symptoms may also include diarrhea, constipation, abdominal pain, and fatigue. Identifying and avoiding trigger foods, keeping a food diary, and seeking guidance from a healthcare professional can help manage food sensitivity bloating.
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
Causes of Bloating:
1. Dietary Factors: Consuming gas-producing foods like beans, broccoli, cabbage, and carbonated beverages can contribute to bloating.
2. Digestive Disorders: Conditions such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), celiac disease, and gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) can cause bloating.
3. Hormonal Changes: Menstruation, pregnancy, and hormonal fluctuations can lead to water retention and bloating.
4. Medical Conditions: Conditions like constipation, intestinal parasites, and certain medications can also contribute to bloating.
Symptoms of Bloating:
1. Abdominal distension or swelling
2. Excessive gas and flatulence
3. Abdominal pain or discomfort
4. Feeling of fullness or tightness in the abdomen
5. Belching or burping
6. Changes in bowel habits, such as diarrhea or constipation
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
Prevention of Bloating:
1. Dietary Modifications: Avoiding gas-producing foods and incorporating more fiber-rich foods can help prevent bloating.
2. Eating Habits: Eating smaller, more frequent meals and chewing food slowly can aid digestion and reduce bloating.
3. Hydration: Drinking an adequate amount of water helps prevent water retention and bloating.
4. Physical Activity: Regular exercise promotes healthy digestion and reduces bloating.
5. Stress Management: Practicing relaxation techniques such as yoga or meditation can help alleviate bloating associated with stress.
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
Treatment Options for Bloating:
1. Over-the-Counter Medications: Antacids, simethicone, and digestive enzymes can help alleviate bloating and gas.
2. Probiotics: Supplements containing beneficial bacteria can improve gut health and reduce bloating.
3. Prescription Medications: For individuals with underlying digestive disorders like IBS, prescription medications may be necessary to manage symptoms.
4. Dietary Changes: Eliminating trigger foods and following a low FODMAP diet under the guidance of a healthcare professional can help reduce bloating.
5. Lifestyle Modifications: Stress reduction techniques, regular exercise, and adequate hydration can also be effective in managing bloating.
Conclusion:
Bloating is a common digestive complaint that can significantly impact quality of life if left untreated. By understanding the causes, symptoms, prevention strategies, and treatment options for bloating, individuals can take proactive steps to manage this condition effectively and improve their overall digestive health. Always consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice and treatment recommendations tailored to your specific needs.