Click here to Visit Facebook Page
Introduction:
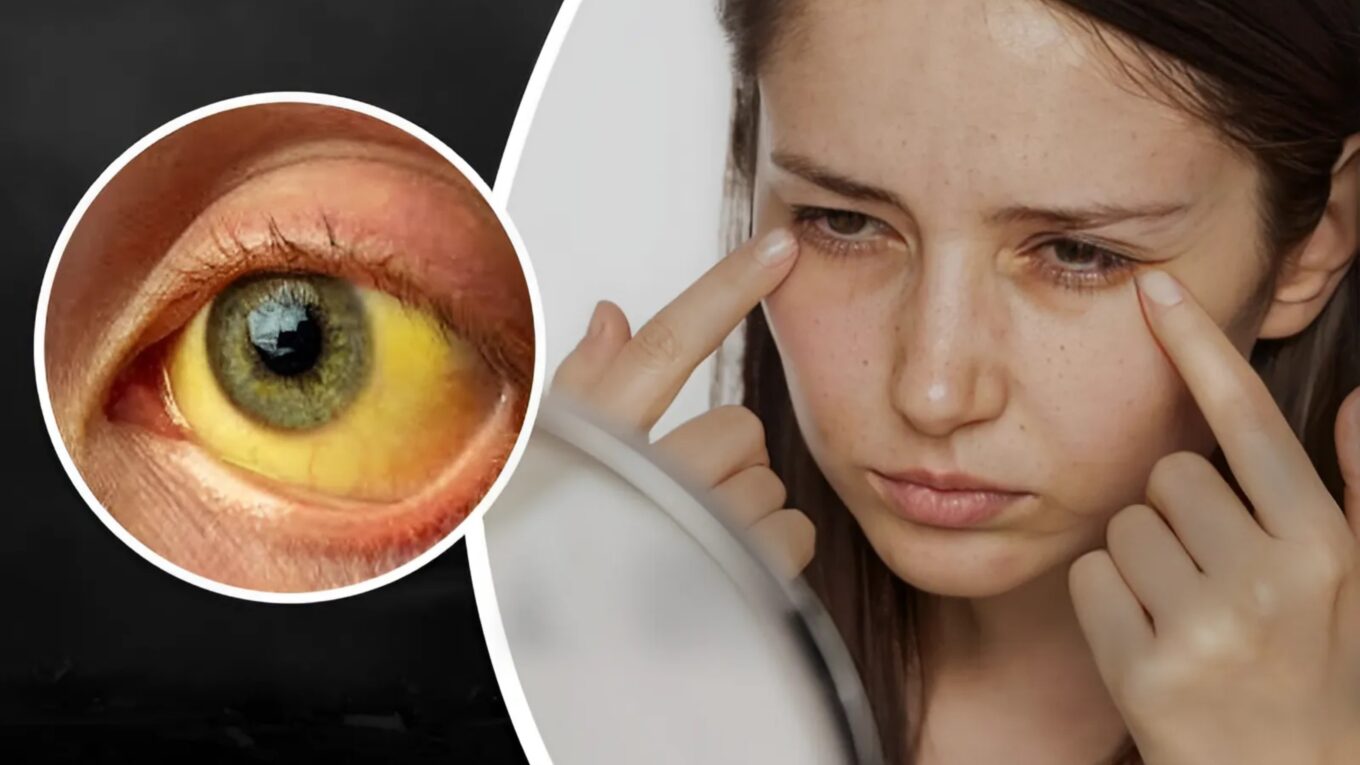
Jaundice is a common medical condition characterized by yellowing of the skin, sclera (the white part of the eyes), and mucous membranes.
It occurs when there is an excess buildup of bilirubin in the bloodstream. Bilirubin is a yellow pigment produced during the normal breakdown of red blood cells. In this blog post, we will delve into the various aspects of jaundice, including its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options.
Causes of Jaundice:
Jaundice can be caused by various factors, including:
1. Hepatitis: Hepatitis is inflammation of the liver, which can be caused by viral infections
(such as hepatitis A, B, or C), alcohol abuse, autoimmune diseases, or exposure to toxins.
2. Liver cirrhosis: Cirrhosis is a late stage of scarring (fibrosis) of the liver caused by many forms of liver diseases and conditions, such as hepatitis and chronic alcoholism.
3. Biliary tract disorders: Conditions affecting the bile ducts, such as gallstones, tumors, or strictures, can obstruct the flow of bile from the liver, leading to jaundice.
4. Hemolytic anemia: This condition occurs when red blood cells are destroyed faster than they are produced, leading to an increase in bilirubin levels.
5. Gilbert’s syndrome: This is a benign genetic disorder characterized by intermittent episodes of jaundice due to reduced bilirubin processing by the liver.
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
Symptoms of Jaundice:
The primary symptom of jaundice is yellowing of the skin, eyes, and mucous membranes. Other symptoms may include:
1. Fatigue and weakness
2. Abdominal pain or discomfort
3. Dark urine
4. Pale stools
5. Itchy skin
6. Nausea and vomiting
Diagnosis of Jaundice:
To diagnose jaundice, a healthcare professional will perform a physical examination and may order the following tests:
1. Blood tests: Blood tests can measure levels of bilirubin, liver enzymes, and other markers of liver function.
2. Imaging tests: Imaging tests such as ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI may be used to visualize the liver, bile ducts, and gallbladder to identify any obstructions or abnormalities.
3. Liver biopsy: In some cases, a liver biopsy may be performed to obtain a sample of liver tissue for further evaluation under a microscope.
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
Treatment of Jaundice:
Treatment for jaundice depends on the underlying cause and may include:
1. Treating the underlying condition: If jaundice is caused by hepatitis, liver cirrhosis, or other liver diseases,
treatment will focus on managing these conditions with medications, lifestyle changes, or in severe cases, liver transplantation.
2. Symptom management: Medications may be prescribed to relieve symptoms such as itching or nausea. Additionally, maintaining adequate hydration and nutrition is important.
3. Phototherapy: In newborns with jaundice, phototherapy may be used to break down excess bilirubin in the bloodstream. During phototherapy, the baby is placed under special lights that emit blue-green wavelengths.
4. Surgery:
In cases where jaundice is caused by an obstruction in the bile ducts, surgery may be necessary to remove the obstruction or bypass it.
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
Prevention of Jaundice:
While some causes of jaundice, such as genetic disorders, cannot be prevented, there are steps you can take to reduce your risk of developing jaundice:
1. Practice safe sex and avoid sharing needles to prevent hepatitis infections.
2. Limit alcohol consumption to reduce the risk of liver damage.
3. Maintain a healthy diet and exercise regularly to support liver health.
4. Follow proper safety precautions when handling toxins or chemicals that may harm the liver.
Conclusion:
Jaundice is a common medical condition that can occur due to various underlying causes, including liver disease, hemolytic anemia, and biliary tract disorders. It is important to seek medical attention if you experience symptoms of jaundice, as early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent complications and improve outcomes. By understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for jaundice, individuals can take proactive steps to maintain their liver health and overall well-being.