Click here to Visit Facebook Page
Introduction:
Celiac disease, a chronic autoimmune disorder triggered by the ingestion of gluten,
remains a perplexing yet prevalent condition affecting approximately 1% of the global population.
Despite its relatively widespread occurrence, navigating the intricacies of celiac disease—from
its onset to its management—demands a comprehensive understanding of
its symptoms, diagnosis, treatment modalities, and coping strategies.
In this exploration, we delve into the multifaceted landscape of celiac disease, shedding light on its nuanced
manifestations and empowering individuals to navigate its challenges with resilience and confidence.
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
Understanding Celiac Disease:
At its core, celiac disease manifests as an immune-mediated reaction to gluten,
a protein abundantly found in wheat, barley, and rye.
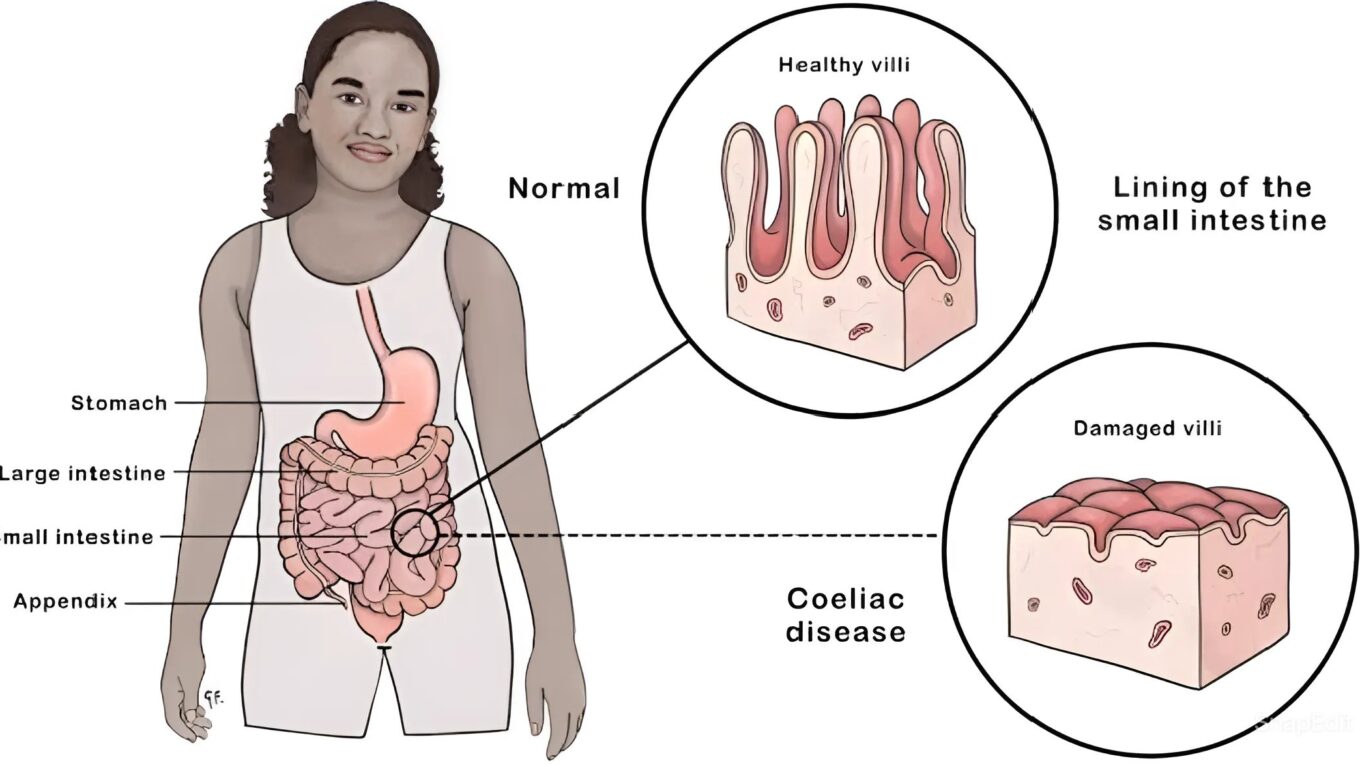
Upon ingestion, gluten triggers an aberrant immune response, leading to inflammation and damage to the small intestine’s lining.
This erosion of the intestinal villi compromises nutrient absorption,
culminating in a spectrum of symptoms ranging from gastrointestinal distress to systemic manifestations.
While the precise etiology of celiac disease remains elusive,
a confluence of genetic predisposition and environmental factors is believed to underpin its development.
Certain genetic markers, such as HLA-DQ2 and HLA-DQ8, confer an increased susceptibility to celiac disease,
highlighting the interplay between genetics and environmental triggers.
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
Symptoms of Celiac Disease:
The symptomatic presentation of celiac disease is diverse and can vary widely among individuals.
Gastrointestinal symptoms, including diarrhea, abdominal pain, bloating, and constipation, are hallmark features of the condition,
often prompting individuals to seek medical attention.
However, celiac disease extends beyond the confines of the gastrointestinal tract, manifesting in extraintestinal symptoms such as
fatigue, weight loss, anemia, dermatitis herpetiformis (a chronic skin rash), and neurological manifestations like headaches and cognitive impairment.
In children, celiac disease may impair growth and development,
underscoring the pervasive impact of this condition across various domains of health.
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
Diagnosing Celiac Disease:
Accurate diagnosis of celiac disease hinges on a meticulous evaluation encompassing clinical history,
physical examination, serological testing, and confirmatory intestinal biopsy.
Initial screening involves serological assays to detect specific antibodies indicative of celiac disease, including anti-tissue transglutaminase (tTG) and anti-endomysial antibodies (EMA). Positive serological findings warrant further investigation through an intestinal biopsy, which reveals characteristic histological changes such as villous atrophy, crypt hyperplasia, and intraepithelial lymphocytosis. The gold standard for diagnosis remains the demonstration of these histological alterations in conjunction with positive serological markers, ensuring a definitive and accurate assessment of celiac disease.
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
Treatment of Celiac Disease:
Central to the management of celiac disease is the adoption of a strict gluten-free diet, the sole effective treatment for mitigating symptoms and averting long-term complications. Eliminating gluten-containing foods from one’s diet is imperative to halt the immune-mediated cascade triggered by gluten ingestion. This entails meticulous label reading, vigilant avoidance of cross-contamination, and adherence to gluten-free substitutes. While embarking on a gluten-free lifestyle may initially pose challenges, the proliferation of gluten-free products and the burgeoning awareness surrounding celiac disease have facilitated the transition for individuals navigating this dietary regimen. In cases of refractory celiac disease or severe complications, adjunctive therapies such as corticosteroids or immunosuppressants may be warranted to alleviate symptoms and mitigate inflammation.
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
Complications of Celiac Disease:
Untreated or inadequately managed celiac disease predisposes individuals to a myriad of complications, spanning nutritional deficiencies, osteoporosis, infertility, neurological disorders, and an increased risk of certain malignancies, notably intestinal lymphoma. Malabsorption of essential nutrients, particularly iron, calcium, and vitamin D, can precipitate anemia, osteoporosis, and other systemic sequelae, underscoring the importance of timely diagnosis and intervention. Moreover, the chronic inflammation perpetuated by gluten exposure may exacerbate autoimmune conditions and heighten susceptibility to secondary health ailments. By prioritizing strict adherence to a gluten-free diet and vigilant monitoring of symptoms, individuals with celiac disease can mitigate these risks and optimize their long-term health outcomes.
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
Living with Celiac Disease:
Embracing a gluten-free lifestyle necessitates a proactive approach encompassing dietary vigilance, lifestyle modifications, and ongoing education. This entails equipping oneself with knowledge about gluten sources, advocating for one’s dietary needs in social settings, and fostering a supportive network of peers and healthcare providers. While the prospect of adhering to a gluten-free diet may initially seem daunting, the growing array of gluten-free products and resources has empowered individuals with celiac disease to navigate their dietary restrictions with confidence and creativity. Furthermore, cultivating resilience and embracing a positive mindset can serve as invaluable assets in the journey of living with celiac disease, enabling individuals to surmount challenges and embrace life to the fullest.
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
Conclusion:
Celiac disease represents a multifaceted entity characterized by immune-mediated reactivity to gluten and systemic manifestations spanning various organ systems. By unraveling the complexities of celiac disease—from its diverse symptomatology to its diagnostic nuances and therapeutic interventions—we empower individuals to confront this condition with knowledge, resilience, and agency. Through steadfast adherence to a gluten-free lifestyle, vigilant monitoring of symptoms, and proactive engagement with healthcare professionals, individuals with celiac disease can navigate its challenges with grace and resilience, reclaiming control over their health and well-being. With heightened awareness, support, and advocacy, the narrative surrounding celiac disease can evolve from one of adversity to one of empowerment, fostering a community of individuals equipped to thrive despite the challenges posed by this autoimmune condition.