Click here to Visit Facebook Page
Introduction:
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is a progressive lung condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It’s a complex disease with significant implications for those diagnosed, as well as their caregivers. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and management of COPD.
Understanding COPD:
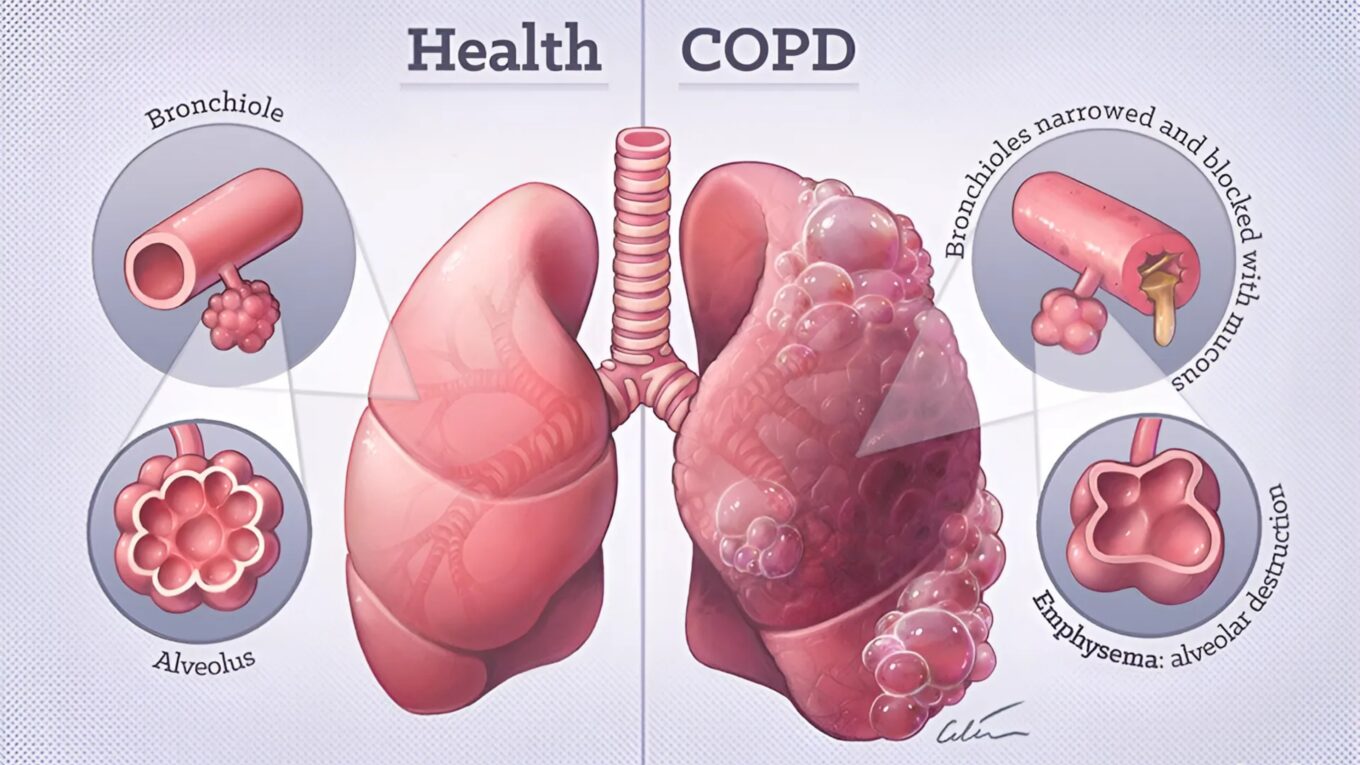
COPD encompasses a group of lung diseases that cause airflow obstruction and breathing-related problems. The two most common forms of COPD are chronic bronchitis and emphysema. Chronic bronchitis involves long-term inflammation of the airways, leading to excess mucus production, while emphysema damages the air sacs in the lungs, reducing their elasticity.
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
Causes of COPD:
The primary cause of COPD is cigarette smoking, accounting for approximately 85-90% of cases. However, long-term exposure to other lung irritants such as air pollution, secondhand smoke, chemical fumes, and dust can also contribute to the development of COPD. In some cases, genetic factors and rare genetic conditions like alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency can predispose individuals to COPD.
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
Symptoms of COPD:
COPD symptoms often develop gradually and worsen over time. Common symptoms include:
1. Chronic cough
2. Shortness of breath, especially during physical activity
3. Wheezing
4. Chest tightness
5. Frequent respiratory infections
6. Fatigue
7. Bluish tint to the lips or fingernail beds (cyanosis) in severe cases
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
Diagnosis of COPD:
Diagnosing COPD typically involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, lung function tests, and imaging studies. Lung function tests, such as spirometry, are crucial for assessing airflow obstruction and determining the severity of the disease. Chest X-rays or CT scans may also be performed to evaluate lung damage and rule out other conditions.
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
Management and Treatment:
While COPD is not curable, various treatment options can help manage symptoms, improve quality of life, and slow disease progression. Treatment strategies may include:
1. Smoking cessation:
Quitting smoking is the most important step in managing COPD and slowing its progression. Smoking cessation programs, counseling, and medications can aid in this process.
2. Medications:
Bronchodilators, such as long-acting beta agonists (LABAs) and anticholinergics, help relax the muscles around the airways, making breathing easier. Inhaled corticosteroids may be prescribed to reduce airway inflammation. Additionally, oral corticosteroids and antibiotics may be used to manage exacerbations and respiratory infections.
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
3. Pulmonary rehabilitation:
Pulmonary rehabilitation programs combine exercise training, education, and counseling to improve lung function, increase exercise tolerance, and enhance overall well-being.
4. Oxygen therapy:
Supplemental oxygen therapy may be prescribed for individuals with severe COPD to alleviate symptoms and improve oxygen levels in the blood.
5. Surgery:
In some cases, surgical interventions such as lung volume reduction surgery or lung transplantation may be considered for select patients with advanced COPD.
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
Lifestyle Modifications:
In addition to medical treatment, certain lifestyle modifications can help individuals with COPD manage their condition more effectively:
1. Avoiding lung irritants:
Minimizing exposure to cigarette smoke, air pollution, and other lung irritants is essential for preventing further lung damage.
2. Staying active:
Regular physical activity, tailored to individual abilities, can improve lung function, endurance, and overall health.
3. Eating a healthy diet:
A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help support lung function and maintain a healthy weight.
4. Monitoring symptoms:
Regular monitoring of COPD symptoms and adherence to treatment plans can help identify exacerbations early and prevent complications.
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
Conclusion:
COPD is a chronic lung condition that requires lifelong management, but with proper diagnosis, treatment, and lifestyle modifications, individuals with COPD can lead fulfilling lives. Early detection and intervention are crucial for optimizing outcomes and improving quality of life for those affected by this debilitating disease. If you or a loved one experience symptoms of COPD, seek medical attention promptly for evaluation and personalized management strategies.