Click here to Visit Facebook Page
Understanding Arthritis and It’s types.
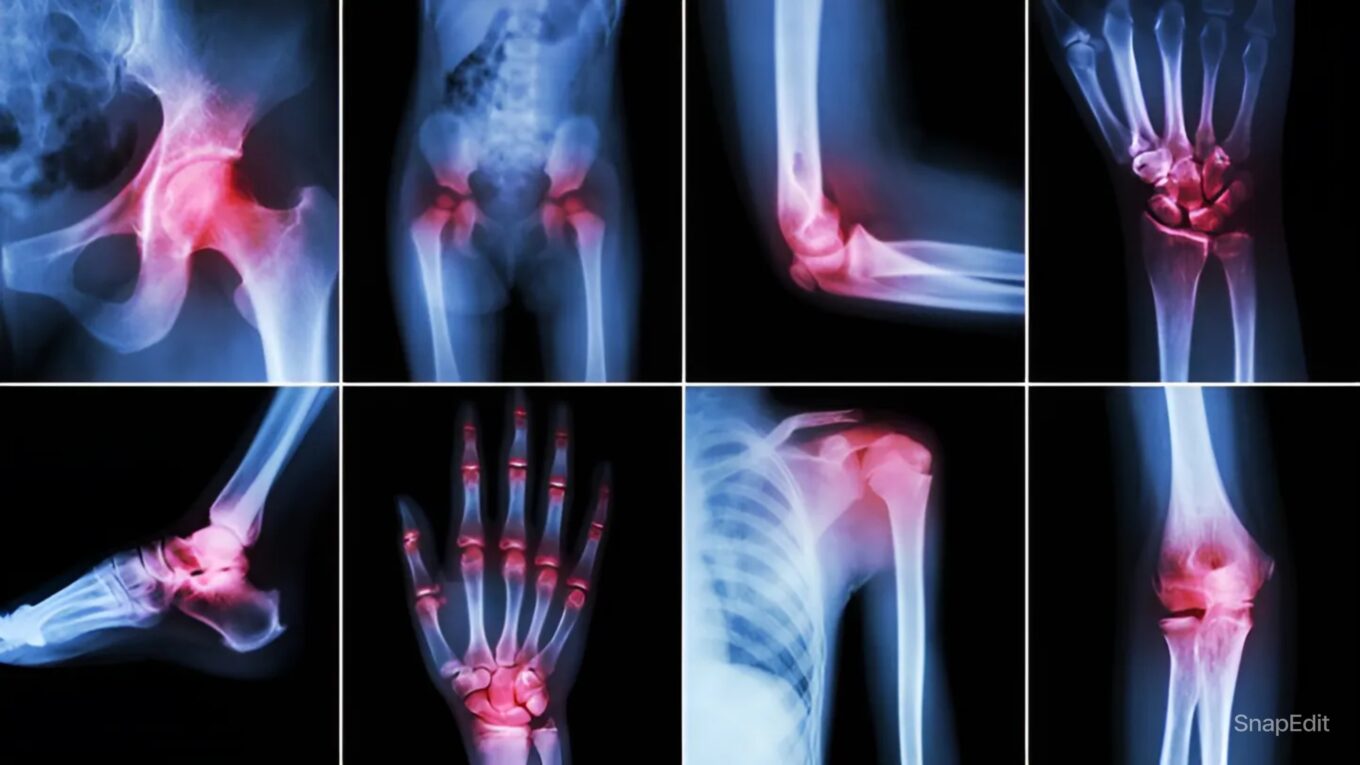
Arthritis is a broad term encompassing more than 100 different conditions characterized by inflammation of the joints.
It affects people of all ages, genders, and ethnic backgrounds, with varying degrees of severity.
This blog aims to provide a comprehensive overview of arthritis,
its types, symptoms, causes, and available treatment options.
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
What is Arthritis?
Arthritis is not a single disease but a term that refers to joint pain or joint disease.
Common symptoms include swelling, pain, stiffness, and decreased range of motion in the joints.
Symptoms can be mild, moderate, or severe, and they may come and go or remain constant.
Severe arthritis can result in chronic pain, inability to perform daily activities,
and make walking or climbing stairs difficult.
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
Types of Arthritis:
The most common types of arthritis include osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, and gout.
Each type has distinct characteristics, causes, and treatments.
1. Osteoarthritis (OA):
– Description:
OA is the most common form of arthritis, often referred to as degenerative joint disease. It occurs when the cartilage that cushions the ends of the bones in the joints deteriorates over time.
– Causes:
Age, joint injury, obesity, genetics, and overuse of the joints.
– Symptoms:
Joint pain and stiffness, particularly after activity; loss of flexibility; grating sensation; bone spurs.
– Treatment:
Lifestyle changes (weight loss, exercise), pain relief medications (acetaminophen, NSAIDs),
physical therapy, and in severe cases, joint replacement surgery.
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
2. Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA):
– Description:
RA is an autoimmune disorder where the immune system attacks the synovium
(the lining of the membranes that surround the joints), causing inflammation and joint damage.
– Causes:
The exact cause is unknown, but genetic and environmental factors play a role.
– Symptoms:
Swollen, tender, and warm joints; joint stiffness, especially in the morning; fatigue, fever, and weight loss.
– Treatment:
Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), biologic agents, NSAIDs, corticosteroids, and physical therapy.
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
3. Psoriatic Arthritis (PsA):
– Description:
PsA is a type of arthritis that affects some people with psoriasis,
a condition that features red patches of skin topped with silvery scales.
– Causes:
Exact cause unknown; genetic, immune system, and environmental factors contribute.
– Symptoms:
Joint pain, stiffness, and swelling; fatigue; psoriasis patches on the skin; nail changes.
– Treatment:
NSAIDs, DMARDs, biologics, and lifestyle changes.
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
4. Gout:
– Description:
Gout is a form of arthritis characterized by sudden, severe attacks of pain, redness,
and tenderness in joints, often the big toe.
– Causes:
Excess uric acid in the blood, which can form sharp, needle-like urate crystals in a joint or surrounding tissue.
– Symptoms:
Intense joint pain, lingering discomfort, inflammation, and redness.
– Treatment:
NSAIDs, colchicine, corticosteroids, lifestyle changes
(diet, weight loss), and medications to lower uric acid levels.
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
Other Types of Arthritis:
– Ankylosing Spondylitis:
A type of inflammatory arthritis affecting the spine and large joints.
– Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis:
The most common type of arthritis in children under the age of 16.
– Lupus:
An autoimmune disease that can cause inflammation in various parts of the body, including the joints.
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
Symptoms of Arthritis:
Common symptoms across different types of arthritis include:
– Pain
– Swelling
– Reduced range of motion
– Stiffness
– Redness
Specific symptoms may vary depending on the type of arthritis.
For example, RA often affects smaller joints first (e.g., fingers, toes), while OA typically affects larger,
weight-bearing joints (e.g., knees, hips).
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
Causes and Risk Factors:
The causes of arthritis vary depending on the type:
– Genetics:
Certain types of arthritis, like RA and lupus, can run in families.
– Age:
The risk of many types of arthritis, including OA, increases with age.
– Gender:
Women are more likely to develop RA, while men are more prone to gout.
– Joint Injuries:
Previous joint injuries can increase the risk of arthritis.
– Obesity:
Excess weight can contribute to both the onset and progression of arthritis.
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
Diagnosis:
Diagnosis typically involves:
– Medical history and physical examination.
– Laboratory tests (e.g., blood tests for RA, uric acid levels for gout).
– Imaging tests (X-rays, MRI, ultrasound) to detect joint damage.
Treatment Options:
Treatment aims to reduce symptoms and improve joint function. It can include:
1. Medications:
– Pain relievers: Acetaminophen, NSAIDs.
– Anti-inflammatory drugs: NSAIDs, corticosteroids.
– Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs): Methotrexate, sulfasalazine.
– Biologic response modifiers: TNF inhibitors, IL-6 inhibitors.
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
2. Therapies:
– Physical Therapy:
Exercises to maintain joint flexibility and muscle strength.
– Occupational Therapy:
Techniques to protect joints and improve daily function.
Surgery:
– Joint Repair:
Smoothing or realigning bones.
– Joint Replacement:
Removing damaged joint and replacing it with a prosthesis.
– Joint Fusion:
Permanently fusing two or more bones together.
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
Lifestyle and Home Remedies:
– Exercise:
Regular physical activity to maintain flexibility and muscle strength.
– Diet:
Eating a balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods.
– Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight to reduce joint stress.
– Heat and Cold Therapy:
Using heat pads or cold packs to relieve pain and stiffness.
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
Alternative Treatments:
Acupuncture:
Can help reduce arthritis pain.
Supplements:
Glucosamine and chondroitin supplements may help some people with OA.
Living with Arthritis:
Living with arthritis requires a comprehensive approach to manage symptoms and maintain quality of life:
– Education:
Understanding the disease and treatment options.
– Support:
Joining support groups or seeking counseling.
– Self-Management:
Learning techniques to manage pain and stay active.
– Assistive Devices:
Using canes, braces, or special tools to ease daily activities.
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
Conclusion:
Arthritis is a complex group of conditions with a wide range of symptoms and impacts.
Early diagnosis and a personalized treatment plan are crucial for managing the disease effectively.
By combining medical treatments with lifestyle changes and supportive therapies,
individuals with arthritis can lead active and fulfilling lives.
If you suspect you have arthritis or are experiencing joint pain, consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment plan.