Click here to Visit Facebook Page
Understanding everything about Phlebitis. Phlebitis is a medical condition characterized by inflammation of a vein. This inflammation can lead to various complications if not managed properly. In this blog, we’ll delve into the types of phlebitis, their causes, symptoms, treatments, and preventive measures.
Types of Phlebitis:
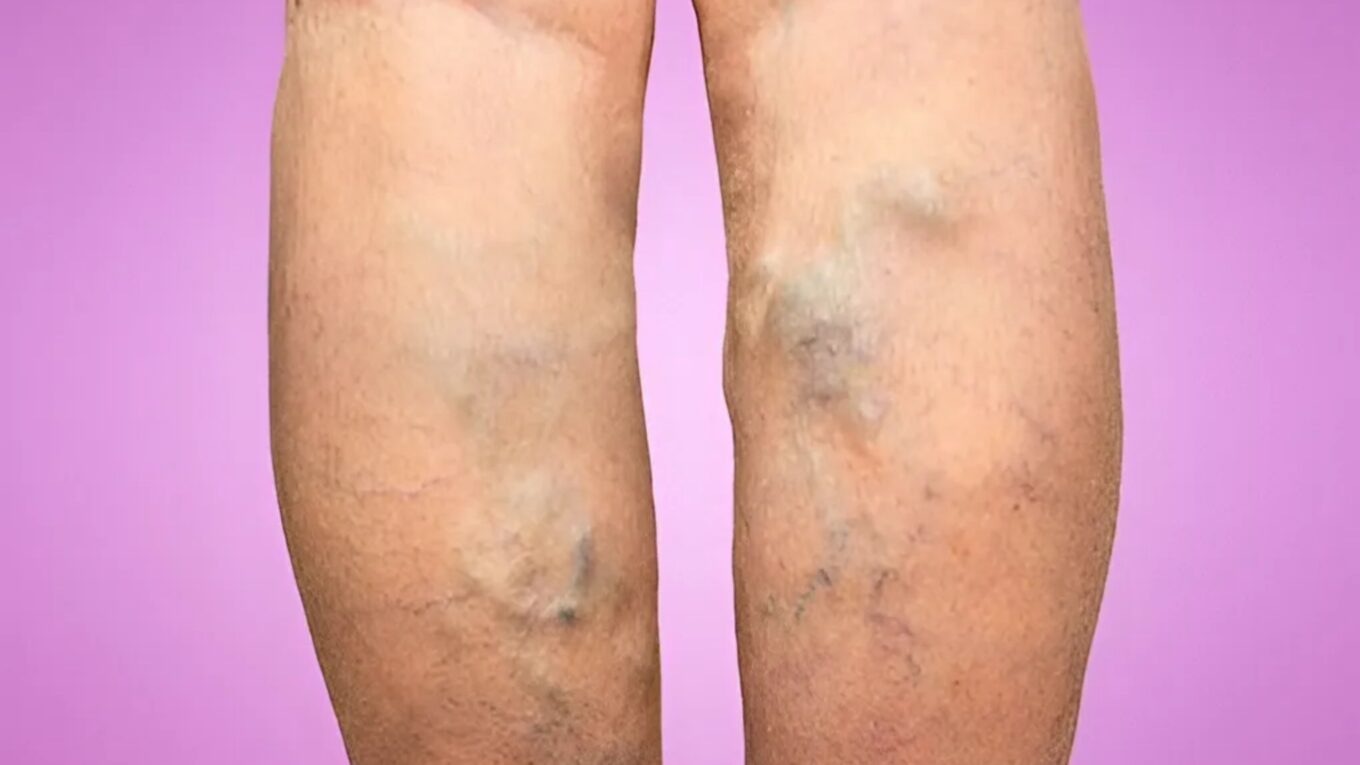
1. Superficial Phlebitis: This affects veins close to the surface of the skin. It is generally less serious but can be painful and cause swelling.
2. Deep Vein Thrombophlebitis (DVT): This occurs in deeper veins, usually in the legs. It is more serious due to the risk of blood clots traveling to the lungs, causing a potentially fatal condition known as pulmonary embolism.
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
Causes of Phlebitis:
Phlebitis can be caused by various factors, including:
– Injury or Trauma: Physical injury or trauma to a vein, such as from an IV catheter, can lead to phlebitis.
– Infection: Bacterial infections can inflame a vein.
– Prolonged Inactivity: Long periods of immobility, such as during a long flight, can lead to blood pooling in the veins, increasing the risk of phlebitis.
– Medical Conditions: Conditions like varicose veins or blood clotting disorders can predispose someone to phlebitis.
– Medications: Certain medications that irritate the veins can cause inflammation.
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
Symptoms of Phlebitis:
The symptoms of phlebitis can vary depending on whether it is superficial or deep.
Superficial Phlebitis:
– Redness and warmth along the affected vein
– Pain or tenderness over the vein
– Swelling in the surrounding area
– A palpable, hard cord-like structure under the skin
Deep Vein Thrombophlebitis:
– Swelling in the leg or affected area
– Pain and tenderness in the leg
– Warmth over the affected vein
– Red or discolored skin
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
Diagnosis:
Diagnosing phlebitis typically involves:
– Physical Examination: Doctors will examine the affected area for signs of inflammation.
– Ultrasound: To visualize blood flow and detect clots in the veins.
– Blood Tests: To check for underlying conditions like clotting disorders or infections.
Treatment Options:
The treatment for phlebitis depends on its severity and underlying cause.
For Superficial Phlebitis:
– Compression Stockings: To improve blood flow and reduce swelling.
– Anti-inflammatory Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can alleviate pain and reduce inflammation.
– Warm Compresses: Applied to the affected area to relieve pain.
– Elevation: Raising the affected limb to reduce swelling.
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
For Deep Vein Thrombophlebitis:
– Anticoagulants: Blood thinners to prevent clot formation.
– Thrombolytic Therapy: Medications to dissolve clots.
– Compression Stockings: To prevent further clotting and reduce swelling.
– Surgery: In severe cases, surgical intervention may be required to remove clots.
Complications:
If untreated, phlebitis can lead to complications such as:
– Chronic Venous Insufficiency: Poor blood flow in the veins over a long period.
– Pulmonary Embolism: A life-threatening condition where a blood clot travels to the lungs.
– Post-Thrombotic Syndrome: Long-term pain and swelling in the affected limb.
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
Prevention:
Preventing phlebitis involves adopting a few key practices:
– Stay Active: Regular exercise helps maintain healthy blood flow.
– Avoid Prolonged Inactivity: Move around during long trips and take breaks to walk if you’re sitting for extended periods.
– Hydrate: Drink plenty of fluids to keep your blood from thickening.
– Wear Compression Stockings: Particularly if you have a history of vein problems.
– Monitor Vein Health: Regular check-ups if you have risk factors like varicose veins or a clotting disorder.
Conclusion:
Phlebitis, though common, should not be taken lightly, especially when it involves deep veins. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and treatment options can help in managing this condition effectively. If you experience any symptoms of phlebitis, it’s crucial to seek medical attention promptly to prevent complications. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle with regular exercise, hydration, and routine medical check-ups can significantly reduce the risk of developing phlebitis.