Click here to Visit Facebook Page
Introduction:
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) are among the most prevalent bacterial infections affecting individuals worldwide. Despite their common occurrence, UTIs can cause significant discomfort and, if left untreated, lead to more severe complications. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricate details of UTIs, exploring their causes, symptoms, treatment modalities, and effective prevention strategies.
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
1. Unraveling the Causes of UTIs:
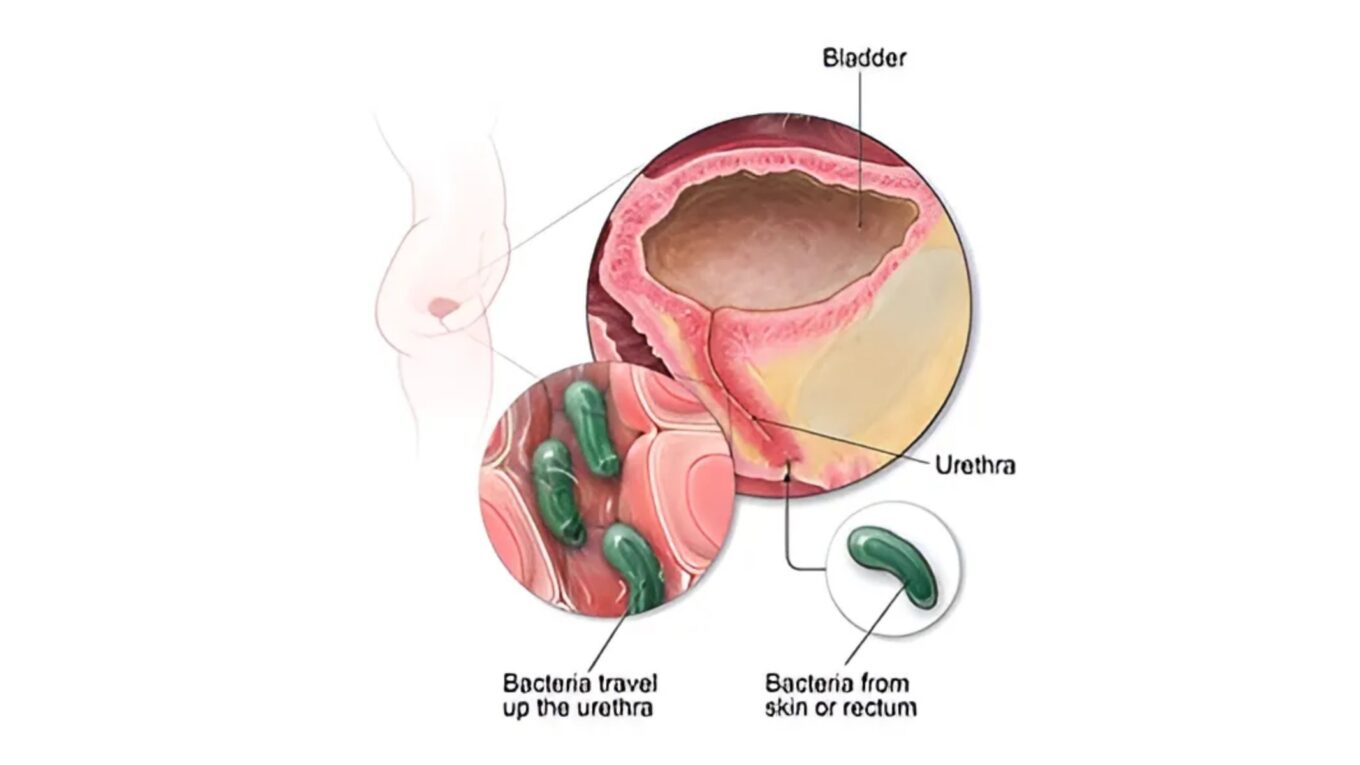
UTIs originate when bacteria infiltrate the urinary tract, precipitating an inflammatory response and subsequent infection. The primary culprit behind UTIs is Escherichia coli (E. coli), a bacterium predominantly residing in the gastrointestinal tract. Various factors predispose individuals to UTIs, including:
– Sexual activity, which may introduce bacteria into the urinary system.
– Hormonal fluctuations, as observed during pregnancy or menopause, altering the urinary tract’s pH balance.
– Certain contraceptive methods, such as diaphragms or spermicides, heightening the risk of bacterial colonization.
– Inadequate bladder emptying, leading to urinary retention and fostering bacterial growth within the urinary tract.
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
2. Deciphering the Symptoms of UTIs:
UTIs often manifest through a spectrum of symptoms, including:
– Dysuria, characterized by a painful or burning sensation during urination.
– Increased frequency of urination, often accompanied by diminished urine output.
– Urinary urgency, prompting a compelling need to urinate even when the bladder is not full.
– Altered urine characteristics, such as cloudiness, foul odor, or the presence of blood (hematuria).
– Pelvic discomfort in women or rectal pain in men.
– Systemic manifestations like fever or chills, signifying a potentially severe infection extending to the kidneys.
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
3. Diagnostic Approaches for UTIs:
Upon suspecting a UTI based on clinical presentation, healthcare providers typically employ diagnostic tests to confirm the diagnosis and guide treatment decisions. These may include urinalysis to assess urine composition for signs of infection, such as bacteria or white blood cells. In certain cases, urine cultures may be conducted to identify the specific pathogenic organism responsible for the infection and determine its antibiotic susceptibility profile, facilitating targeted therapy.
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
4. Navigating UTI Treatment Options:
The cornerstone of UTI management revolves around antibiotic therapy aimed at eradicating the causative bacterial pathogen. The selection of antibiotics and treatment duration hinges on various factors, including the severity of the infection, bacterial susceptibility patterns, and the patient’s medical history. It is imperative for individuals to adhere rigorously to the prescribed antibiotic regimen, completing the full course even if symptoms abate prematurely, to prevent recurrence and minimize the emergence of antibiotic resistance.
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
5. Empowering UTI Prevention Strategies:
While UTIs may not always be entirely preventable, adopting certain proactive measures can mitigate the risk of their occurrence:
– Hydration: Maintaining adequate fluid intake facilitates frequent urination, flushing out potential pathogens from the urinary tract.
– Hygiene Practices: Practicing meticulous personal hygiene, including proper genital cleansing and wiping from front to back after using the restroom, can deter bacterial entry into the urinary tract.
– Urination Habits: Emptying the bladder before and after sexual activity, avoiding prolonged periods of urine retention, and ensuring complete bladder evacuation during urination can help thwart bacterial colonization.
– Clothing Choices: Opting for breathable cotton undergarments and loose-fitting attire promotes genital hygiene by minimizing moisture retention and enhancing ventilation.
– Prophylactic Measures: Consideration of single-dose antibiotic prophylaxis may be warranted in specific high-risk scenarios, such as recurrent UTIs or before urological procedures, to preemptively suppress bacterial growth.
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
Conclusion:
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) represent a prevalent health concern with significant implications for affected individuals. By fostering a comprehensive understanding of UTIs, encompassing their etiology, clinical manifestations, diagnostic strategies, therapeutic interventions, and preventive measures, individuals can empower themselves to navigate these infections effectively. Prompt recognition of UTI symptoms, coupled with timely medical evaluation and adherence to preventive practices, is paramount in averting complications and preserving urinary tract health.