Click here to Visit Facebook Page
Introduction:
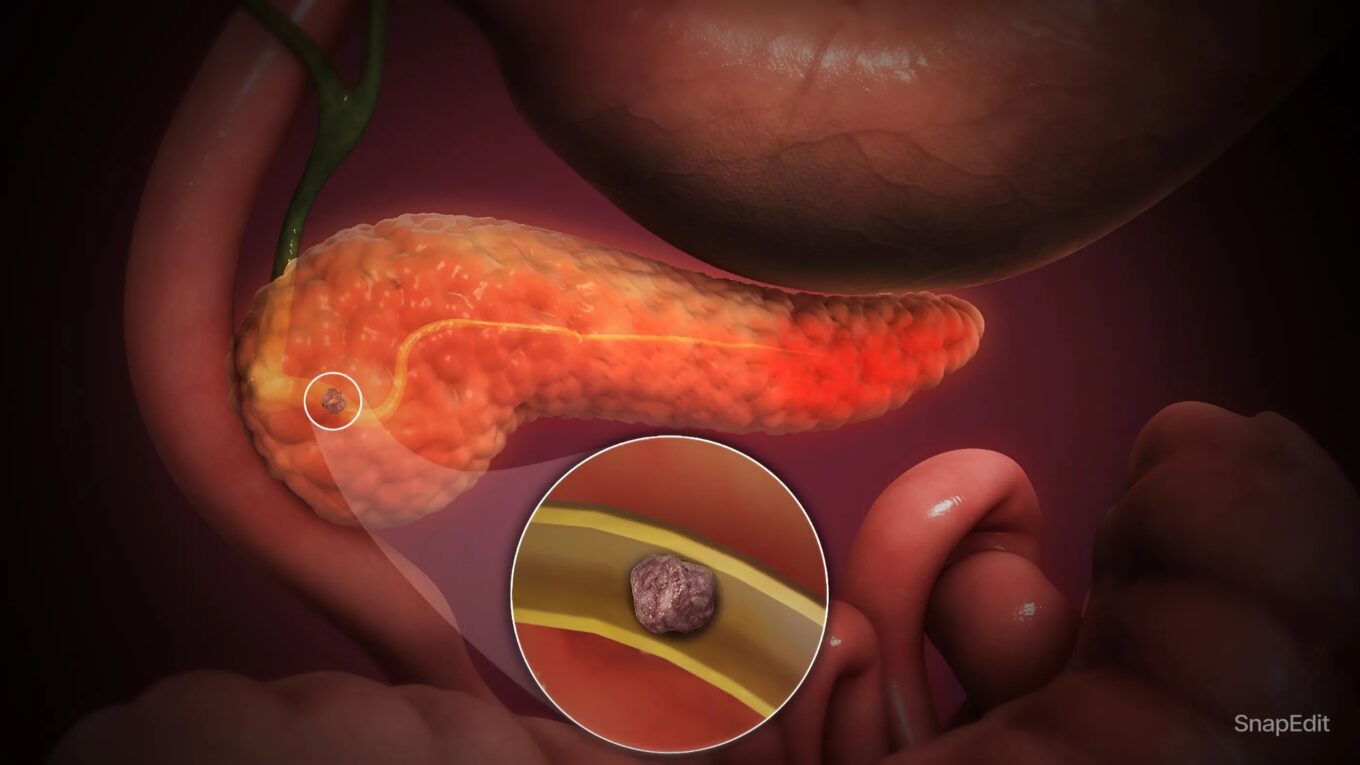
The Ultimate Guide to Pancreatitis. Pancreatitis is an inflammatory condition of the pancreas, an organ located behind the stomach that plays a crucial role in digestion and blood sugar regulation. This blog will explore the different types of pancreatitis, their causes, symptoms, diagnostic methods, and treatment options, providing a comprehensive overview of this potentially serious condition.
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
What is Pancreatitis?
Pancreatitis occurs when the pancreas becomes inflamed. This inflammation can happen suddenly (acute pancreatitis) or over many years (chronic pancreatitis). The pancreas produces digestive enzymes that help break down food in the small intestine. It also releases hormones like insulin and glucagon that help regulate blood sugar levels.
Types of Pancreatitis:
1. Acute Pancreatitis:
This type develops quickly and can be severe. It often results in abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, fever, and a rapid pulse. Most cases are mild and resolve with appropriate medical treatment, but severe cases can cause life-threatening complications.
2. Chronic Pancreatitis:
This is a long-lasting inflammation of the pancreas that alters its normal structure and functions. It often follows repeated episodes of acute pancreatitis. Over time, it can lead to permanent damage, resulting in the loss of both digestive and endocrine functions of the pancreas.
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
Causes of Pancreatitis:
Pancreatitis can be triggered by various factors, including:
– Gallstones: These are one of the most common causes of acute pancreatitis. They can block the bile duct, trapping digestive enzymes in the pancreas and causing inflammation.
– Alcohol Abuse: Chronic and excessive alcohol consumption is a major cause of both acute and chronic pancreatitis. It can lead to the premature activation of pancreatic enzymes, damaging the organ.
– Genetic Factors: Certain genetic mutations can increase the risk of developing pancreatitis, particularly chronic pancreatitis.
– Medications: Some drugs can cause pancreatitis as a side effect.
– Infections: Infections such as mumps can lead to pancreatitis.
– Trauma: Abdominal injury can result in inflammation of the pancreas.
– Metabolic Disorders: Conditions such as hypertriglyceridemia and hypercalcemia can also trigger pancreatitis.
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
Symptoms of Pancreatitis:
The symptoms of pancreatitis vary depending on whether the condition is acute or chronic.
– Acute Pancreatitis:
– Severe abdominal pain that radiates to the back
– Nausea and vomiting
– Fever
– Rapid pulse
– Tenderness when touching the abdomen
– Chronic Pancreatitis:
– Persistent abdominal pain that may worsen after eating
– Weight loss without trying
– Oily, smelly stools (steatorrhea)
– Diabetes (due to the loss of insulin-producing cells)
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
Diagnosing Pancreatitis:
Diagnosing pancreatitis typically involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests:
– Blood Tests: Elevated levels of pancreatic enzymes (amylase and lipase) in the blood can indicate pancreatitis.
– Imaging Tests: Various imaging techniques, such as abdominal ultrasound, CT scan, MRI, and endoscopic ultrasound, can help visualize the pancreas and detect inflammation, gallstones, or other abnormalities.
– Stool Tests: For chronic pancreatitis, stool tests can measure the fat content to assess the pancreas’s ability to digest fats.
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
Treatment of Pancreatitis:
The treatment of pancreatitis depends on the severity and underlying cause of the condition.
Acute Pancreatitis:
– Hospitalization: Most patients with acute pancreatitis require hospitalization. Treatment focuses on supporting the body’s functions and allowing the pancreas to heal.
– Fasting: Patients may need to fast for a few days to rest the pancreas. Nutritional support may be provided via IV fluids or a feeding tube if necessary.
– Pain Management: Pain relief is a critical aspect of treatment.
– Fluids and Electrolytes: IV fluids are administered to maintain hydration and electrolyte balance.
– Treating the Underlying Cause: If gallstones are the cause, procedures like endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) or surgery may be necessary to remove the stones.
Chronic Pancreatitis:
– Lifestyle Changes: Avoiding alcohol and smoking, following a low-fat diet, and eating small, frequent meals can help manage symptoms.
– Medications: Pain relief and pancreatic enzyme supplements can aid digestion.
– Insulin Therapy: If diabetes develops, insulin therapy may be required.
– Surgery: In severe cases, surgery may be needed to drain fluid collections, remove obstructions, or resect part of the pancreas.
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
Complications of Pancreatitis:
Both acute and chronic pancreatitis can lead to complications, including:
– Pancreatic Pseudocysts: Fluid-filled sacs that can become infected or rupture.
Infection: Infected pancreatic tissue can require surgical removal.
– Breathing Problems: Inflammation can affect lung function.
– Diabetes: Chronic pancreatitis can damage insulin-producing cells.
– Malnutrition: Chronic pancreatitis can interfere with digestion and nutrient absorption.
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
Preventing Pancreatitis:
Prevention strategies focus on addressing the risk factors:
– Limit Alcohol Consumption: Reducing alcohol intake can significantly lower the risk of pancreatitis.
– Maintain a Healthy Diet: A balanced diet low in fat and high in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help.
– Regular Exercise: Maintaining a healthy weight through regular exercise can prevent gallstones and other metabolic issues.
– Manage Medical Conditions: Properly managing conditions like high triglycerides and diabetes can reduce the risk.
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
Conclusion:
Pancreatitis is a serious condition that requires timely diagnosis and appropriate management to prevent complications and improve quality of life. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options can help individuals take proactive steps to maintain pancreatic health and seek medical attention when necessary. If you experience persistent abdominal pain or other symptoms associated with pancreatitis, consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment plan.