Click here to Visit Facebook Page
Introduction:
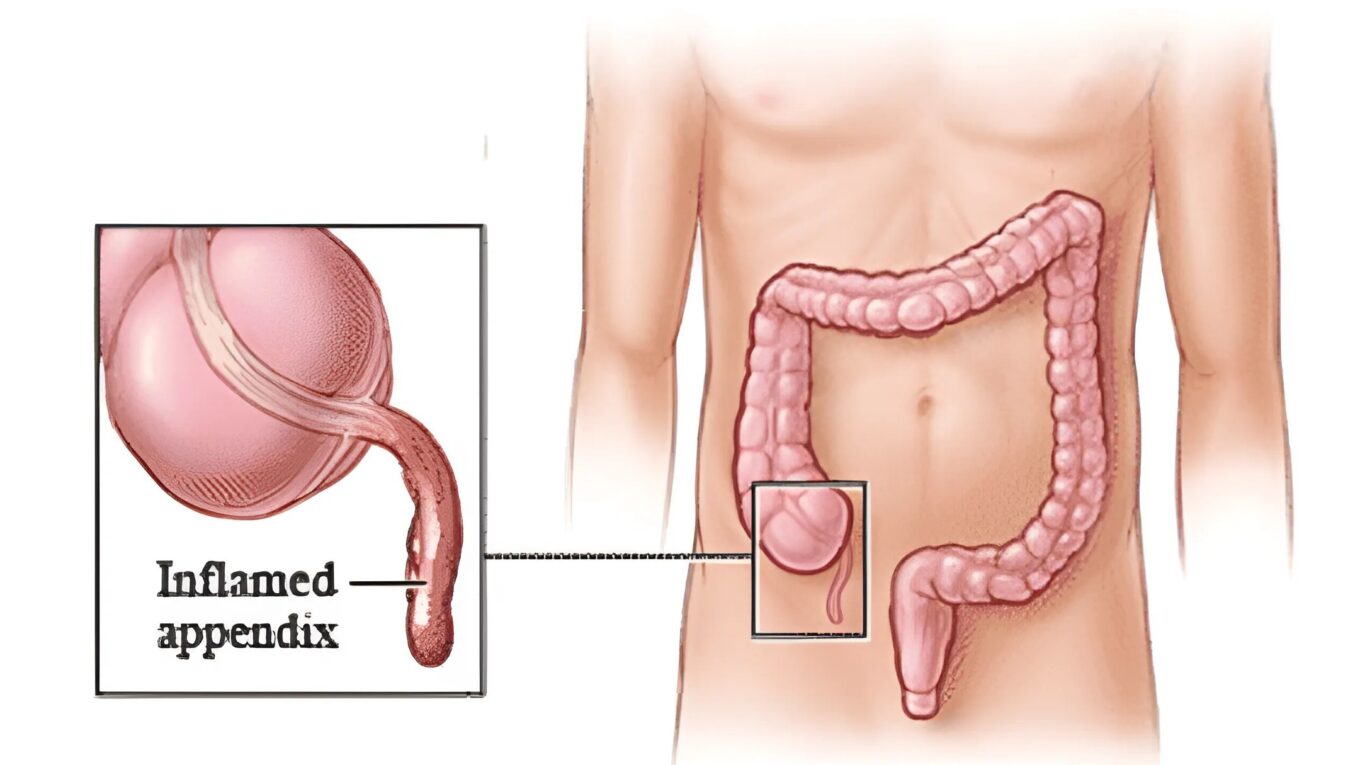
Appendicitis is a medical condition characterized by the inflammation of the appendix, a small pouch attached to the large intestine. While the exact cause of appendicitis remains unclear, it is essential to recognize its symptoms, understand its potential complications, and seek prompt medical attention. In this blog post, we will delve into the various aspects of appendicitis, including its symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and treatment options.
Symptoms:
Appendicitis often manifests through a variety of symptoms, which may include:
1. Abdominal pain: The most common symptom of appendicitis is pain around the belly button that later shifts to the lower right side of the abdomen.
2. Nausea and vomiting: Many individuals with appendicitis experience nausea and may vomit as a result.
3. Loss of appetite: People with appendicitis may find themselves with a decreased appetite.
4. Fever and chills: In some cases, appendicitis can lead to a low-grade fever accompanied by chills.
5. Changes in bowel habits: Appendicitis may cause diarrhea or constipation, or a combination of both.
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
Causes:
The exact cause of appendicitis is not always clear, but it is often associated with the blockage of the appendix. This blockage can occur due to various factors, including:
1. Fecal matter: Blockage of the appendix can occur when hard stools or fecal matter become trapped inside, leading to inflammation and infection.
2. Enlarged lymphoid follicles: The appendix contains lymphoid tissue, which can become enlarged and block the appendix, particularly in younger individuals.
3. Tumors: Rarely, tumors within the appendix or nearby structures can cause obstruction and subsequent appendicitis.
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
Diagnosis:
Diagnosing appendicitis typically involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests. Healthcare providers may:
1. Conduct a physical exam: Physicians will often palpate the abdomen to assess for tenderness and pain, particularly in the lower right quadrant.
2. Order blood tests: Blood tests, including a complete blood count (CBC), may reveal an elevated white blood cell count, indicating an inflammatory response.
3. Perform imaging studies: Imaging tests such as ultrasound or computed tomography (CT) scans can help visualize the appendix and confirm the diagnosis of appendicitis.
Treatment:
The treatment of appendicitis usually involves surgical removal of the inflamed appendix, known as an appendectomy. This procedure can be performed through traditional open surgery or minimally invasive laparoscopic surgery. In some cases, if the appendix has not yet ruptured, antibiotics may be prescribed to reduce inflammation and infection.
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
Complications:
If left untreated, appendicitis can lead to serious complications, including:
1. Ruptured appendix: If the inflamed appendix bursts, it can release bacteria and toxins into the abdominal cavity, leading to a potentially life-threatening condition known as peritonitis.
2. Abscess formation: In some cases, pus may accumulate around the appendix, forming an abscess that requires drainage and additional treatment.
3. Sepsis: Severe infection from a ruptured appendix can lead to sepsis, a systemic inflammatory response that can be life-threatening if not promptly treated.
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
Prevention:
While appendicitis cannot always be prevented, there are some steps individuals can take to reduce their risk, including:
1. Eating a high-fiber diet: Consuming plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help maintain regular bowel movements and prevent fecal impaction.
2. Staying hydrated: Drinking an adequate amount of water can help prevent constipation and maintain bowel health.
3. Seeking prompt medical attention: If experiencing symptoms suggestive of appendicitis, it is essential to seek medical evaluation promptly to prevent complications.
Conclusion:
Appendicitis is a common medical emergency that requires prompt recognition and treatment. By understanding its symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and treatment options, individuals can take proactive steps to seek appropriate medical care and reduce the risk of complications associated with this condition. If you or someone you know experiences symptoms of appendicitis, it is crucial to contact a healthcare provider immediately for evaluation and management.