Click here to Visit Facebook Page
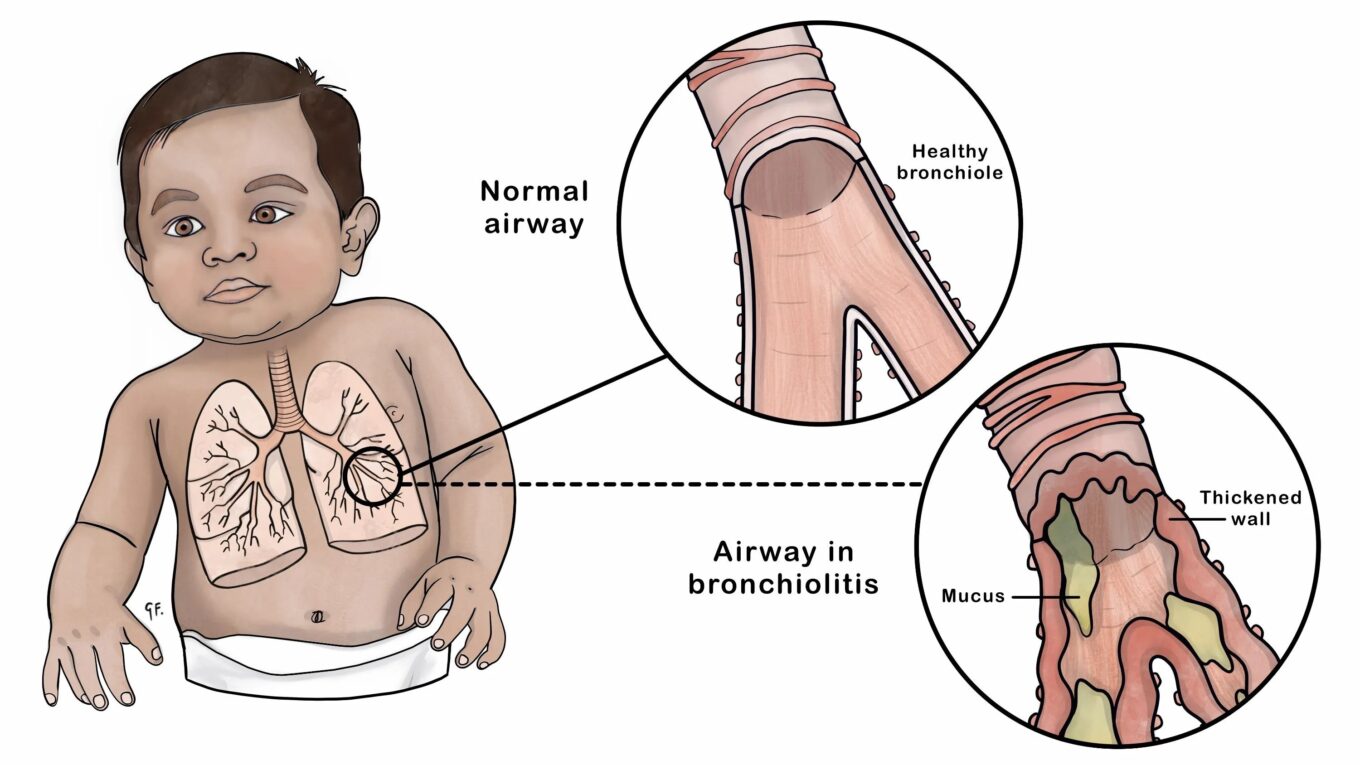
Bronchiolitis is a common respiratory infection that primarily affects infants and young children. It is characterized by inflammation and congestion in the smallest air passages of the lungs, known as the bronchioles. While most cases of bronchiolitis are mild and resolve on their own, severe cases can lead to breathing difficulties and may require medical intervention. In this article, we will delve into the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment of bronchiolitis to help you better understand this condition.
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
Causes of Bronchiolitis:
The most common cause of bronchiolitis is a viral infection, with respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) being the primary culprit. RSV is highly contagious and easily spreads through respiratory droplets when an infected person coughs or sneezes. Other viruses that can cause bronchiolitis include adenovirus, influenza, and human metapneumovirus.
Symptoms of Bronchiolitis:
The symptoms of bronchiolitis often mimic those of a common cold in its early stages but can progress to more severe respiratory distress. Common symptoms include:
1. Runny or stuffy nose
2. Cough
3. Sneezing
4. Fever
5. Wheezing
6. Rapid or difficult breathing
7. Cyanosis (blue-tinged skin due to lack of oxygen)
Infants and young children, especially those under the age of 2, are most susceptible to developing severe symptoms of bronchiolitis.
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
Diagnosis of Bronchiolitis:
A healthcare provider can typically diagnose bronchiolitis based on the child’s symptoms and a physical examination. In some cases, they may order additional tests such as a chest X-ray or a nasal swab to confirm the presence of a viral infection, particularly if the symptoms are severe or if there is concern about complications such as pneumonia.
Treatment of Bronchiolitis:
Since bronchiolitis is caused by a viral infection, antibiotics are not effective in treating the condition. Treatment is usually focused on managing the symptoms and providing supportive care. This may include:
1. Maintaining hydration: Encouraging the child to drink plenty of fluids to prevent dehydration, especially if they have a fever or are having difficulty feeding.
2. Using a humidifier: Using a cool-mist humidifier in the child’s room can help ease congestion and make breathing more comfortable.
3. *Nasal saline drops: Using saline drops or spray can help loosen mucus in the nasal passages, making it easier for the child to breathe.
4. Elevating the head: Keeping the child’s head elevated while sleeping can help reduce congestion and make breathing easier.
5. Monitoring breathing: Parents should closely monitor their child’s breathing and seek medical attention if they notice any signs of respiratory distress, such as rapid breathing, chest retractions, or cyanosis.
In severe cases of bronchiolitis, especially if the child is having significant difficulty breathing, hospitalization may be necessary. In the hospital, the child may receive oxygen therapy, intravenous fluids, or in some cases, respiratory support such as mechanical ventilation.
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
Prevention of Bronchiolitis:
Since bronchiolitis is primarily caused by viral infections, the best way to prevent it is by practicing good hygiene habits to reduce the spread of viruses. This includes:
1. Frequent handwashing: Encourage regular handwashing with soap and water, especially after coughing, sneezing, or touching surfaces in public places.
2. Avoiding close contact with sick individuals: Try to avoid close contact with people who are sick, especially during the peak bronchiolitis season, which typically occurs during the winter months.
3. Limiting exposure to smoke: Avoid exposure to tobacco smoke, as it can exacerbate respiratory symptoms and increase the risk of developing bronchiolitis.
4. Vaccination: While there is currently no vaccine specifically for bronchiolitis, getting vaccinated against the flu (influenza) and ensuring that all recommended childhood vaccinations are up to date can help reduce the risk of developing respiratory infections.
Conclusion:
Bronchiolitis is a common respiratory infection that primarily affects infants and young children. While most cases are mild and resolve on their own, severe cases can lead to breathing difficulties and may require medical intervention. By understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment of bronchiolitis, parents and caregivers can better manage the condition and help prevent its spread. If you suspect that your child may have bronchiolitis, it is important to seek medical attention promptly for proper evaluation and treatment.