Click here to Visit Facebook Page
Introduction:
Leukemia, a term derived from the Greek words “leukos” meaning white,
and “haima” meaning blood, is a complex and potentially life-threatening condition
that affects the blood and bone marrow.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the various aspects of leukemia,
including its causes, types, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options.
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
What is Leukemia?
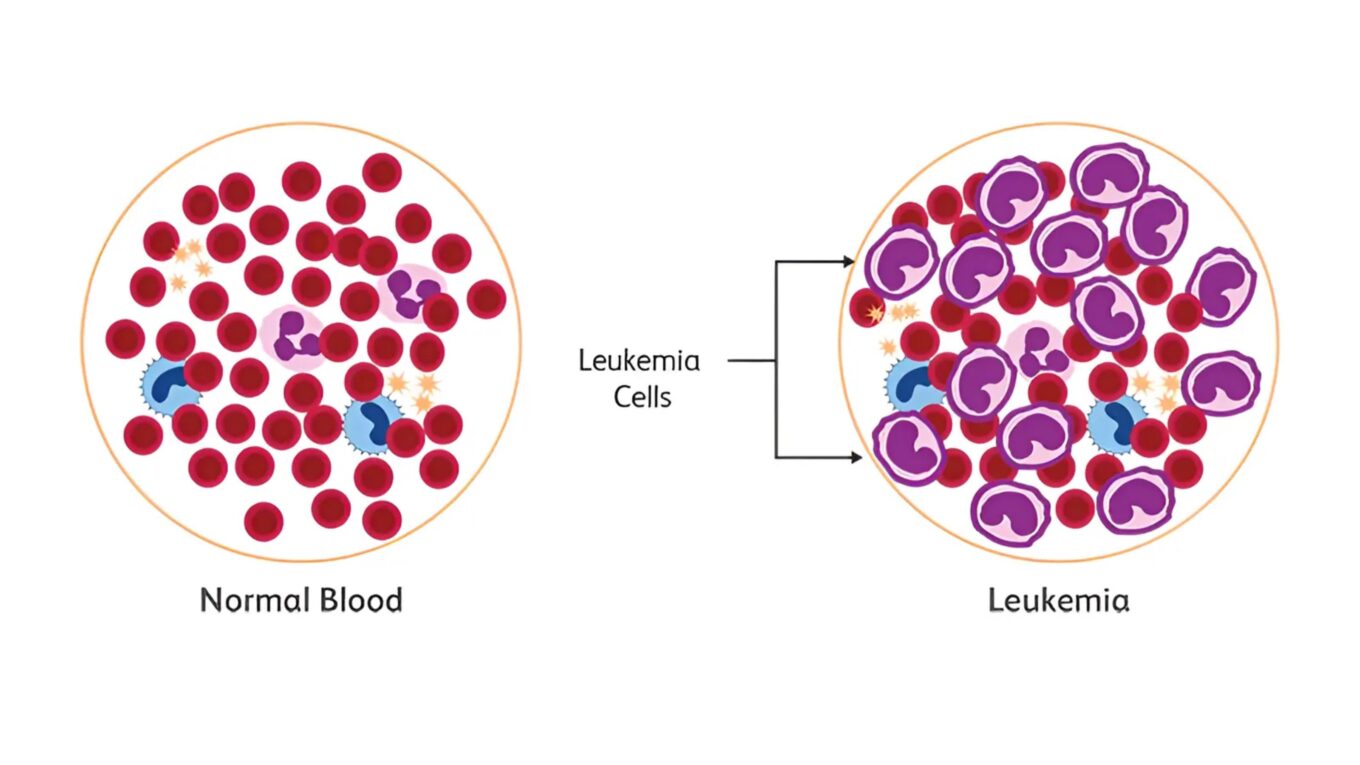
Leukemia is a type of cancer that originates in the bone marrow,
where blood cells are produced.
It affects the body’s ability to produce healthy blood cells,
leading to an abnormal increase in immature white blood cells (leukocytes).
These abnormal cells crowd out healthy blood cells,
impairing the body’s ability to fight infections and deliver oxygen to tissues.
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
Causes of Leukemia:
The exact cause of leukemia remains unknown,
but several factors may increase the risk of developing the condition:
1. Genetic predisposition:
Certain genetic mutations inherited from parents can increase
the likelihood of developing leukemia.
2. Exposure to radiation:
Prolonged exposure to high levels of radiation,
such as from radiation therapy or nuclear accidents, is a known risk factor.
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
3. Chemical exposure:
Exposure to certain chemicals, such as benzene and certain
chemotherapy drugs, may increase the risk of leukemia.
4. Viral infections:
Infections with certain viruses, such as the human T-cell leukemia virus (HTLV-1) or
the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), have been linked to an increased risk of leukemia.
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
Types of Leukemia:
Leukemia is classified into four main types based on the speed of disease
progression and the type of white blood cell affected:
1. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL):
This type of leukemia progresses rapidly and primarily affects lymphoid cells,
which are a type of white blood cell involved in the immune system.
2. Acute myeloid leukemia (AML):
AML is characterized by the rapid growth of abnormal myeloid cells,
which are responsible for producing red blood cells, platelets,
and certain types of white blood cells.
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
3. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL):
CLL progresses slowly and primarily affects mature lymphocytes,
which are a type of white blood cell involved in the immune response.
4. Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML):
CML is characterized by the excessive production of mature and immature granulocytes,
a type of white blood cell involved in the immune response.
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
Symptoms of Leukemia:
The symptoms of leukemia can vary depending on the type and stage of the disease. Common symptoms include:
– Fatigue and weakness
– Frequent infections
– Easy bruising or bleeding
– Swollen lymph nodes
– Fever and night sweats
– Bone pain
– Unexplained weight loss
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
Diagnosis of Leukemia:
Diagnosing leukemia typically involves a combination of physical examinations,
blood tests, and bone marrow tests. Blood tests can detect abnormal levels of white blood cells,
red blood cells, and platelets, while bone marrow tests, such as bone marrow aspiration and biopsy,
can confirm the presence of leukemia cells.
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
Treatment Options:
Treatment for leukemia depends on the type of leukemia,
the patient’s age and overall health, and the stage of the disease.
Common treatment options include:
– Chemotherapy: The use of powerful drugs to kill cancer cells.
– Radiation therapy: High-energy radiation to destroy cancer cells.
– Targeted therapy: Drugs that target specific abnormalities present in cancer cells.
– Immunotherapy: Treatment that helps the immune system recognize and attack cancer cells.
– Stem cell transplantation: Replacement of diseased bone marrow with healthy stem cells to restore normal blood cell production.
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
Conclusion:
Leukemia is a complex and challenging condition that requires
a multidisciplinary approach to diagnosis and treatment.
While significant progress has been made in understanding and treating leukemia,
ongoing research is essential to improve outcomes for patients
and develop more effective therapies.
If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of leukemia,
it is crucial to seek medical attention promptly for proper diagnosis and treatment.