Click here to Visit Facebook Page
Introduction:
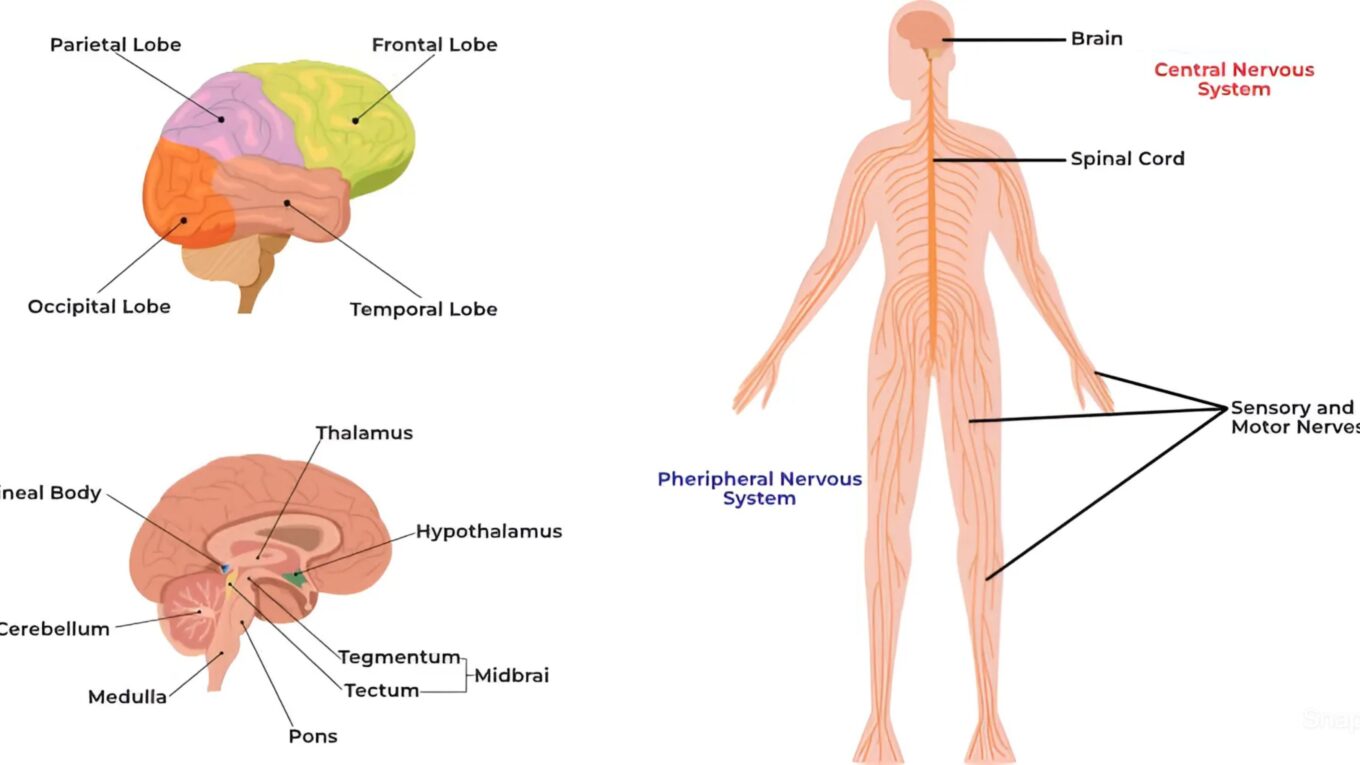
The central nervous system (CNS) serves as the command center of the human body, coordinating and regulating essential functions. Comprised of the brain and spinal cord, the CNS plays a pivotal role in processing sensory information, initiating motor responses, and governing cognitive functions. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the anatomy, function, and disorders of the central nervous system.
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
Anatomy of the Central Nervous System:
1. Brain:
– The brain is the most complex organ in the human body, consisting of billions of neurons and glial cells.
– Divided into several regions, including the cerebrum, cerebellum, brainstem, and diencephalon.
– The cerebrum, responsible for higher cognitive functions such as perception, memory, and reasoning, is divided into two hemispheres, each with four lobes: frontal, parietal, temporal, and occipital.
– The cerebellum coordinates voluntary movements, balance, and posture.
– The brainstem, comprised of the midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata, regulates basic life functions such as breathing, heart rate, and sleep cycles.
– The diencephalon includes the thalamus and hypothalamus, which play key roles in sensory processing, hormone regulation, and homeostasis.
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
2. Spinal Cord:
– The spinal cord is a long, tubular structure extending from the base of the brainstem to the lumbar region of the spine.
– It serves as a conduit for sensory and motor information, transmitting signals between the brain and peripheral nervous system.
– Protected by the vertebral column, the spinal cord consists of gray and white matter, with gray matter housing cell bodies and white matter containing nerve fibers.
– Specific regions of the spinal cord control different bodily functions, with cervical segments regulating upper body movements and lumbar segments controlling lower body movements.
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
Function of the Central Nervous System:
1. Sensory Processing:
– The CNS receives sensory information from the peripheral nervous system via sensory neurons.
– Sensory receptors in the skin, muscles, organs, and other tissues detect stimuli such as touch, temperature, pain, and proprioception.
– This information is transmitted to the brain for interpretation and response.
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
2. Motor Control:
– The CNS initiates voluntary and involuntary motor responses through motor neurons.
– Motor areas of the brain, including the primary motor cortex and basal ganglia, plan and execute movements.
– Reflex arcs, coordinated by the spinal cord, enable rapid, involuntary responses to stimuli without conscious processing.
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
3. Cognitive Functions:
– The CNS governs a wide range of cognitive processes, including perception, attention, memory, language, and decision-making.
– Complex networks of neurons in the cerebral cortex and subcortical structures underlie these cognitive functions.
Common Disorders of the Central Nervous System:
1. Neurodegenerative Diseases:
– Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and Huntington’s disease are characterized by progressive degeneration of neurons, leading to cognitive decline, movement disorders, and other symptoms.
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
2. Stroke:
– A stroke occurs when blood flow to the brain is disrupted, resulting in brain damage and neurological deficits.
– Ischemic strokes, caused by blockages in blood vessels, and hemorrhagic strokes, caused by bleeding in the brain, are the two main types of strokes.
3. Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI):
– TBIs result from sudden, external forces to the head, causing damage to brain tissue.
– Symptoms vary depending on the severity and location of the injury and may include headaches, dizziness, cognitive impairment, and changes in mood or behavior.
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
Conclusion:
The central nervous system is a remarkable and complex network of structures responsible for regulating virtually every aspect of human physiology and behavior. Understanding its anatomy, function, and common disorders is essential for promoting brain health, diagnosing neurological conditions, and developing effective treatments. Continued research into the CNS holds the promise of unlocking new insights into the mysteries of the mind and improving the lives of individuals affected by neurological disorders.