Click here to Visit Facebook Page
Introduction.
Uric acid is a natural waste product formed from the breakdown of purines, which are substances found in certain foods and also produced by the body. While uric acid is typically dissolved in the blood and eliminated through the kidneys, elevated levels can lead to health issues, notably gout and kidney stones. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the causes, symptoms, prevention, and treatment options for high uric acid levels.
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
Causes of High Uric Acid:
1. Dietary Factors:
Consumption of purine-rich foods such as red meat, organ meats, shellfish, and certain types of fish can contribute to elevated uric acid levels.
2. Obesity:
Being overweight or obese is associated with higher levels of uric acid as excess body fat can lead to increased production of uric acid.
3. Genetics:
Some individuals may have a genetic predisposition to higher uric acid levels, making them more susceptible to conditions like gout.
4. Medical Conditions:
Certain medical conditions such as kidney disease, diabetes, hypertension, and metabolic syndrome can elevate uric acid levels.
5. Medications:
Certain medications like diuretics, aspirin, and certain chemotherapy drugs can interfere with uric acid excretion, leading to elevated levels.
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
Symptoms of High Uric Acid:
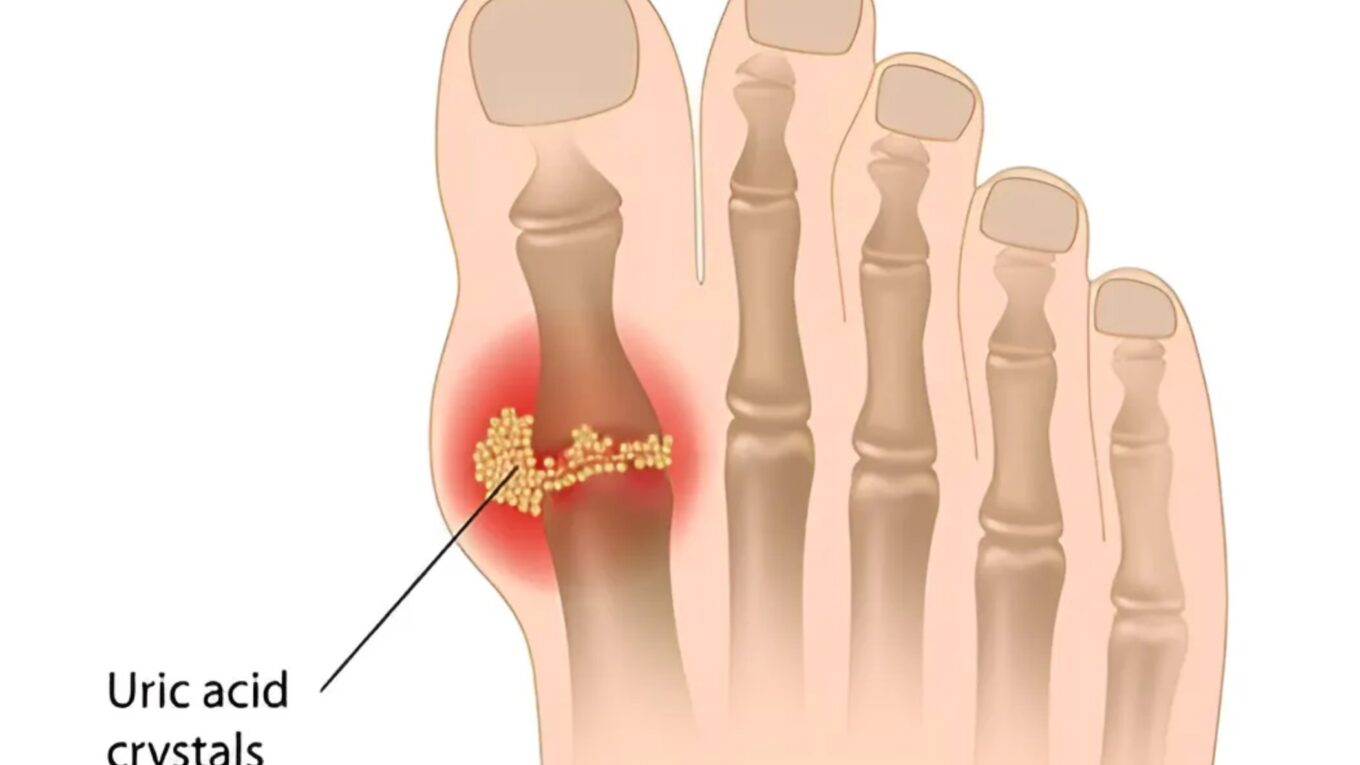
1. Gout:
One of the most common symptoms of high uric acid levels is gout, which is characterized by sudden and severe joint pain, typically in the big toe. The affected joint becomes swollen, red, and extremely tender.
2. Kidney Stones:
Elevated uric acid levels can lead to the formation of urate crystals in the kidneys, which can result in the development of kidney stones. Symptoms include severe pain in the back or side, nausea, vomiting, and blood in the urine.
3. Joint Inflammation:
High uric acid levels can cause inflammation in other joints besides the big toe, such as the ankles, knees, wrists, and elbows.
4. Tophi:
In some cases, urate crystals can accumulate in the soft tissues, forming small, white, chalky lumps known as tophi. These can develop under the skin, around joints, and in other areas of the body.
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
Prevention of High Uric Acid:
1. Healthy Diet:
Adopting a diet low in purine-rich foods and high in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and low-fat dairy products can help prevent high uric acid levels.
2. Stay Hydrated:
Drinking plenty of water helps to flush out uric acid from the body, reducing the risk of crystal formation.
3. Limit Alcohol:
Alcohol consumption, especially beer and spirits, can increase uric acid levels, so it’s advisable to limit intake.
4. Maintain a Healthy Weight:
Losing weight if you are overweight can help reduce uric acid levels and decrease the risk of gout attacks.
5. Regular Exercise:
Engaging in regular physical activity not only helps with weight management but also improves overall health and may help lower uric acid levels.
Click here to Visit Facebook Page
Treatment of High Uric Acid:
1. Medications:
Depending on the severity of the condition, your doctor may prescribe medications such as allopurinol, febuxostat, or probenecid to lower uric acid levels and prevent gout attacks.
2. Pain Management:
During gout attacks, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), colchicine, or corticosteroids may be prescribed to relieve pain and inflammation.
3. Lifestyle Modifications:
In addition to dietary changes and weight management, avoiding triggers such as dehydration, excessive alcohol consumption, and certain medications can help prevent gout attacks.
Conclusion:
High uric acid levels can lead to painful conditions like gout and kidney stones, but with the right lifestyle modifications,
dietary changes, and medical interventions, it is possible to manage and lower uric acid levels effectively. If you experience symptoms of high uric acid or have concerns about your health,
consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice and treatment options.